Publications /
Opinion
The artificial intelligence landscape is undergoing a fundamental shift that most people haven’t yet noticed. While “prompt engineering” has dominated conversations about optimizing AI interactions, a more sophisticated paradigm is quietly emerging: context engineering. This evolution represents more than a semantic change; it signals a transformation in how we architect intelligent systems.
As Andrej Karpathy, former Director of AI at Tesla, explains: “In every industrial-strength LLM app, context engineering is the delicate art and science of filling the context window with just the right information for the next step.” [1] This distinction between casual AI use and production systems reveals why context engineering has become the critical skill that separates functional AI demos from transformative business applications.
From Simple Prompts to Sophisticated Context
Context engineering transcends the limitations of traditional prompt crafting in ways that fundamentally change how AI systems operate. Where prompt engineering focuses on asking the right question, context engineering creates the optimal environment for AI to identify and execute solutions autonomously. The distinction is profound: prompt engineering operates within the context window, while context engineering determines what fills that window [2].
According to groundbreaking research from the Chinese Academy of Sciences, context engineering represents “a formal discipline that transcends simple prompt design to encompass systematic optimization of information payloads for LLMs.” [3] This systematic approach addresses the fundamental challenge of modern AI applications: managing the delicate balance between information richness, computational constraints, and real-world complexity.
The shift reflects hard-won lessons from building production AI systems. As Philipp Schmid explains: “Context Engineering is the discipline of designing and building dynamic systems that provides the right information and tools, in the right format, at the right time, to give a LLM everything it needs to accomplish a task.” [4] This definition emphasizes three critical aspects: it is systematic rather than ad hoc, dynamic rather than static, and comprehensive rather than limited to text instructions.
Consider how this plays out in practice. When you ask an LLM to write an email, you’re doing prompt engineering. But when an AI assistant automatically drafts a personalized response to a customer complaint by accessing purchase history, previous support interactions, company policies, and current inventory levels, that is context engineering.
Contemporary context engineering therefore encompasses nine critical components that work together to create intelligent, context-aware systems [5]:
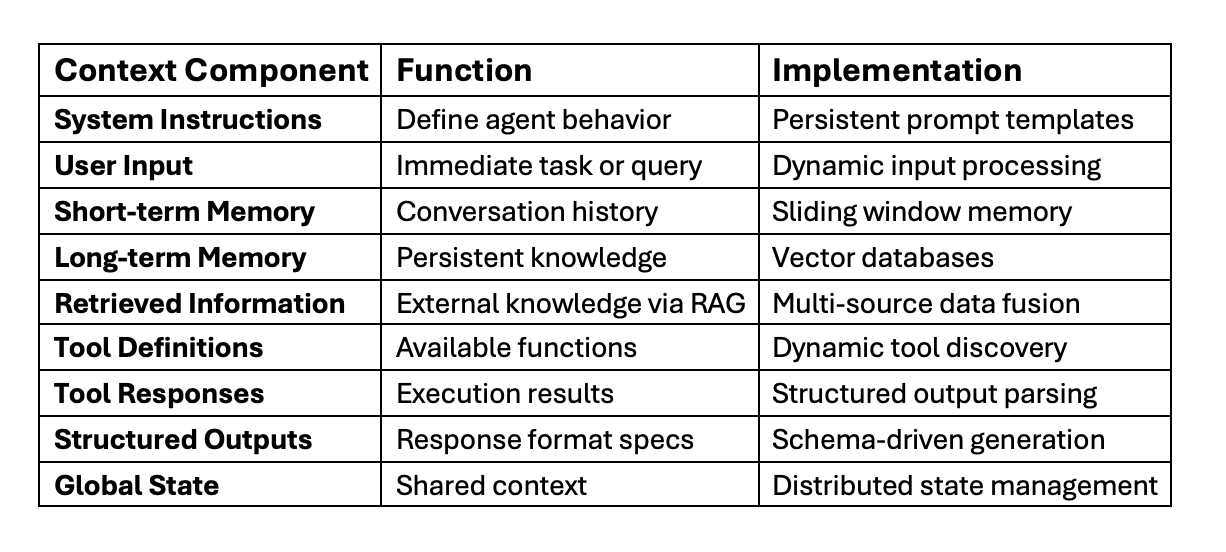
The differentiation between prototype AI applications and production-ready systems lies fundamentally in the quality of context. Research from Kubiya.ai demonstrates how context engineering transforms user experiences [6]. Consider the contrast between these scenarios. A basic AI assistant receives: “Schedule a meeting with the marketing team.” Without context, it replies: “When would you like to schedule this meeting?”
A context-engineered system, however, operates with comprehensive environmental awareness. It knows your calendar, understands your role, has access to team availability, recognizes urgency based on recent communications, and is aware of company preferences. Its response becomes: “I’ve scheduled a marketing strategy session for Thursday 2-3 PM with Ali, Sara, and Omar based on your recent project discussions. The meeting room is booked and the agenda is prepared.”
This transformation—from reactive questioning to proactive solution delivery—exemplifies the production value of context engineering. The AI doesn’t just respond to requests; it anticipates needs, understands implications, and takes comprehensive action based on deep situational awareness.
Solving AI's Context Failures
What makes context engineering particularly revolutionary is its ability to address fundamental limitations that have long plagued AI systems. Traditional prompt-based approaches often suffer from “context failures,” situations where the AI lacks the information needed to make sound decisions [7]. These failures manifest as context poisoning, context distraction, context confusion, and context clash.
Context engineering solves these problems through systematic information architecture. Instead of relying on well-crafted prompts to elicit the right responses, it builds systems that actively curate, validate, and optimize the information environment. This includes relevance-scoring algorithms, contradiction-detection systems, information-freshness tracking, and dynamic context-window management.
Leading AI companies are implementing context-engineering principles at scale. Anthropic notes that “agents often engage in conversations spanning hundreds of turns, requiring careful context management strategies.” [8] This recognition underscores that the most challenging aspects of building production AI systems are not related to model capabilities, but to creating information architectures that enables performance.
The emergence of specialized frameworks such as LangGraph signals industry recognition of this paradigm’s importance [9]. These tools offer structured approaches to implementing the four core context-engineering strategies: write, select, compress, and isolate.
Context engineering represents more than a technical advancement; it embodies a fundamental shift toward intelligent, autonomous systems that operate with human-like situational awareness. For organizations implementing AI solutions designed to deliver value, context engineering isn’t optional.
The revolution is not in the prompts we write, but in the contexts we engineer.
References
[1] Andrej Karpathy, Context Engineering Discussion, 2025 www.github.com/davidkimai/Context-Engineering#context-engineering
[2] Drew Breunig, “Why ‘context engineering’ matters”, 2025 https://www.dbreunig.com/2025/07/24/why-the-term-context-engineering-matters.html
[3] Lingrui Mei et al., “A Survey of Context Engineering for Large Language Models”, arXiv:2507.13334v1, 2025
https://arxiv.org/html/2507.13334v1
[4] Philipp Schmid, “The New Skill in AI is Not Prompting, It’s Context Engineering”, 2025
https://www.philschmid.de/context-engineering
[5] Tuana Çelik, Logan Markewich, “Context Engineering - What it is, and techniques to consider”, LlamaIndex, 2025
https:// www.llamaindex.ai/blog/context-engineering-what-it-is-and-techniques-to-consider
[6] Amit Eyal Govrin, “Context Engineering : The Hidden Blueprint Behind Reliable AI Agents in 2025”, Kubiya.ai, 2025
https://www.kubiya.ai/blog/context-engineering-ai-agents
[7] Lance Martin, “Context Engineering for Agents”, 2025
https://rlancemartin.github.io/2025/06/23/context_engineering/
[8] Anthropic, “Context Engineering for Agents”, LangChain Blog, 2025
https://blog.langchain.com/context-engineering-for-agents/
[9] LangChain Team, “The rise of context engineering”, LangChain Blog, 2025
https://blog.langchain.com/the-rise-of-context-engineering/







