Publications /
Opinion
There are signs of recovery in various parts of the global economy, starting in May, after the depressive dip imposed by Covid-19. Such signs emerged after the easing of restrictions on mobility established to flatten out the pandemic curves, and also reflected policies of flattening the recession curve (income transfers to part of the population, credit lines to vulnerable companies and others).
Besides remaining far from giving back the GDP lost, in all countries, the recovery faces doubts about its strength. There is a similar sequence in each country, but there are differences due to the rhythms of the pandemic and the effectiveness, magnitude, and time length of the policies to flatten out the recession curve. The pace of the pandemic matters not only because of the possibility of returning restrictions on mobility but also because it affects the behavior of consumers. It is not by chance that the signs of recovery are stronger in the manufacturing industry and much weaker in the service segments that involve agglomeration of people.
Take, for example, China – the “first in, first out”. Its GDP grew 3.2% per year in the second quarter, above expectations but still leaving the level of its GDP with a decline of 1.6% in the first half of the year. On the other hand, retail sales disappointed. It should be the only large economy to show growth at the end of the year (1%), but well below what its pre-Covid trajectory pointed out.
It is worth noting the Chinese has resorted to the growth-cum-debt policy that was applied after the global financial crisis of 2008-09 and that led to concerns about its financial stability. Drops on Chinese stock exchanges last Thursday 16th echoed on Wall Street and on stock exchanges in Europe.
Take the case of the United States. The Federal Reserve Bank report - - the"beige book" -released last Wednesday 15th showed increased activity in all districts, but far from pre-Covid levels. Industrial production rose 5.4% in June, to a large extent due to the normalization of production of automobiles and their parts. On the other hand, the high-frequency indicators for services are showing much lower levels than before the pandemic.
Employment levels rose in May and June (2 and 3 million, respectively). However, to a large extent it was the reversal of temporary layoffs, accompanying the return of mobility. Meanwhile, the group of permanent unemployed and job seekers increased by 2 million.
In Europe, the dive caused by Covid-19 was deeper than in the USA and the recovery has been faster. Industrial production fell 29% in March and April, gaining back 14% in May. But, like in China and the U.S, with services lagging.
Now take Brazil as a reference for emerging markets. The fall in GDP in the second quarter was less than expected, among other reasons because the “emergency aid” disbursed by the federal government until the end of May was larger than the losses in the wage bill in the country until then. Doubts arise, however, regarding new positive surprises in the second half of the year, not least because everything will depend on the pace of recovery of informal employment at the end of emergency transfers in August. In the second half of the year, everything will depend on the pace of new infections, as this will continue to negatively affect the economy, not least because consumer behavior tends to reflect that pace regardless of possible returns to mobility restrictions.
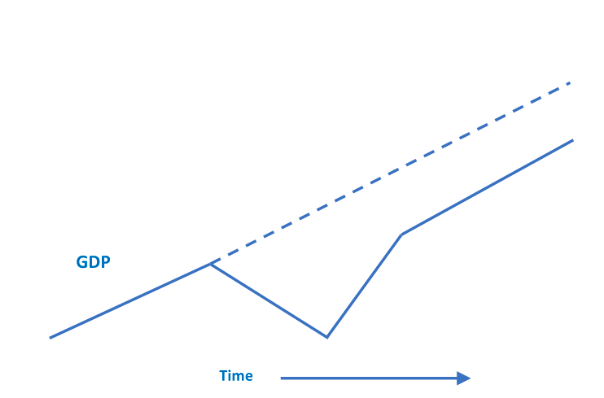
What will be the shape of the economic recovery curve in the different cases? Will any country have a “V”, that is, the return of the economy in a short time to the previous trajectory after suffering a strong blow during the pandemic? Or "U"? Perhaps a "W" if new outbreaks of Covid-19 appear and new rounds of mobility restrictions are established?
Probably the square root sign illustrates the most likely scenario, with some recovery of the lost GDP but not a return to the previous trajectory (see the figure). The surge in demand previously pent-up and released with the relaxation of mobility restrictions is momentary and exhaustible. It is not possible to compensate for dinners in restaurants or trips that did not occur during restrictions. Additionally, as already observed in all countries, the fear of physical proximity (very much grounded on reality) and restrictions on the occupancy of supply capacity will keep limits on the recovery of services.
The period of collapse in economic activity will leave scars in terms of closed firms and jobs that will not return. Fiscal restriction walls impose limits on the time length of policies of flattening the recession curve. It is not by chance that almost all economic projections suggest national GDPs at the end of next year still below last year's levels – likely except for China and India.
Success in crossing the coronavirus crisis will be measured by the proximity - but not return - to the previous GDP trajectory. Thereafter, the task will be to deal with structural unemployment created by changing consumption patterns, increased levels of poverty in much of the world, the concentration of income, the challenges posed by digitalization and the tendency towards relative deglobalization. One should add the need to move toward a “green recovery”. The calculation of the square root will depend on the policies applied in each country.
Otaviano Canuto is a senior fellow at the Policy Center for the New South, a nonresident senior fellow at Brookings Institution, and principal of the Center for Macroeconomics and Development. He is a former vice-president and a former executive director at the World Bank, a former executive director at the International Monetary Fund and a former vice-president at the Inter-American Development Bank. He is also a former deputy minister for international affairs at Brazil’s Ministry of Finance and a former professor of economics at University of São Paulo and University of Campinas, Brazil.





