Publications /
Opinion
Official statistics record more than 4.6 million people as dying of COVID-19 across the world, a population roughly equal to that of New Zealand. About 10,000 people continue to die of the disease every day. Furthermore, there is strong evidence that the number of COVID-19 deaths is underreported in many instances. For example, a continuously updated database of estimated COVID-19 deaths by The Economist suggests that the actual number of deaths across the world could be two to three times the official number.
Official statistics record more than 4.6 million people as dying of COVID-19 across the world, a population roughly equal to that of New Zealand. About 10,000 people continue to die of the disease every day. Furthermore, there is strong evidence that the number of COVID-19 deaths is underreported in many instances. For example, a continuously updated database of estimated COVID-19 deaths by The Economist suggests that the actual number of deaths across the world could be two to three times the official number.
To get a better handle on how many have died of COVID-19, various agencies and news media keep track of excess deaths, the difference between deaths in each period and the expected number of deaths based on historical averages, typically computed over a five-year period, and adjusted for demographic trends. Comparing these numbers with officially reported COVID-19 deaths shows that in some countries, such as in the Russian Federation, excess deaths in 2020 were 6.25 times reported COVID-19 deaths, while in others, such as France, excess deaths were 15% fewer than reported COVID-19 deaths.
There are many reasons why excess death numbers deviate from actual COVID-19 deaths; underreporting is just one possible reason. There is some randomness in mortality data as in any statistic. For example, natural disasters or wars can increase the death count, and the data employed in this note adjusts for these exceptional events where possible (Karlinsky and Kobak, 2021). The pressure on the health system caused by the COVID-19 pandemic may have caused many deaths by hindering the provision of adequate care for other diseases, or by causing some who lost jobs and are confined in lockdowns to consume excessive alcohol or overdose on drugs. Meanwhile, precautions to contain COVID-19, such as wearing masks, keeping a distance, and confinement, may prevent deaths that would have occurred otherwise, for example from traffic accidents or from seasonal flu, both of which phenomena have been observed in the data in countries such as France.
With the caveat that excess deaths are likely to be an imprecise indicator at best of COVID-19 deaths, it is nevertheless striking how the divergence between the two statistics varies across countries. Figure 1 shows the distribution of what we call the undercount ratio (excess deaths/COVID-19 deaths) for the 71 countries for which mortality data is available for 2020. The figure shows that the undercount ratio was less than 1, i.e., excess deaths were below reported COVID-19 deaths, in only 17 countries, a group which includes advanced countries such as Denmark, but also developing countries such as Tunisia, Peru, and Argentina. At the other end of the distribution, the undercount ratio was greater than 3, i.e., excess deaths were over three times reported COVID-19 deaths, in 11 countries, all of which are former republics of the Soviet Union, with Egypt the sole exception in that group.
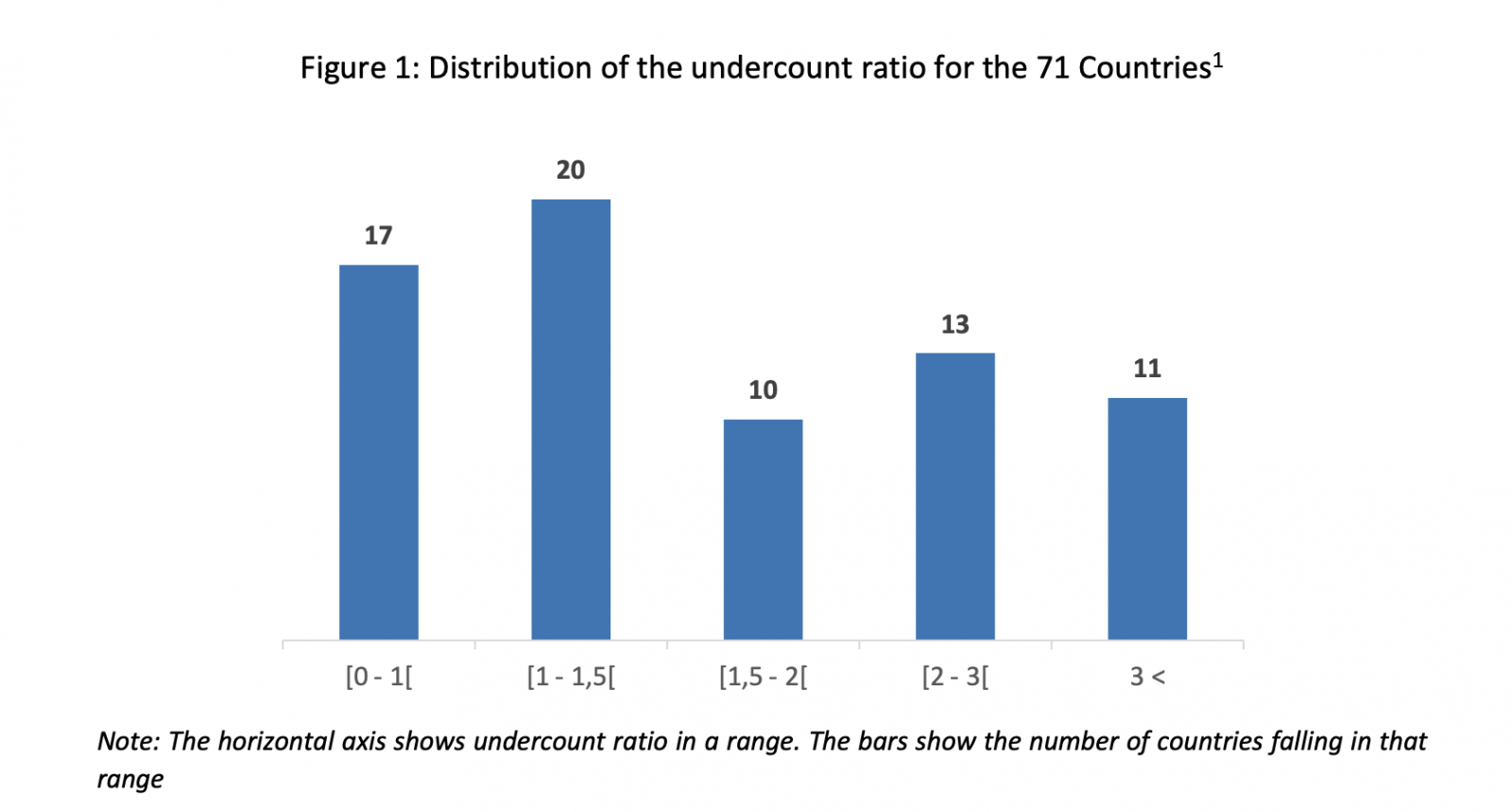
We can exploit the very large variation of the undercount ratio across countries to evaluate what might cause COVID-19 deaths to be underreported, or over-reported. Unfortunately, the excess data statistic for 2020 is not yet available for very large countries such as China and India, and nor is it available for Morocco, for example.
At least three important factors might account for underreporting, which appears to be the far more frequent occurrence in our sample. First, many people die of COVID-19 without being diagnosed. This would be especially the case in countries where the hospital system is under strain, for example. A second reason could be low statistical capacity, the case in many poor countries[2]. A third possible reason is government reluctance to communicate bad news.
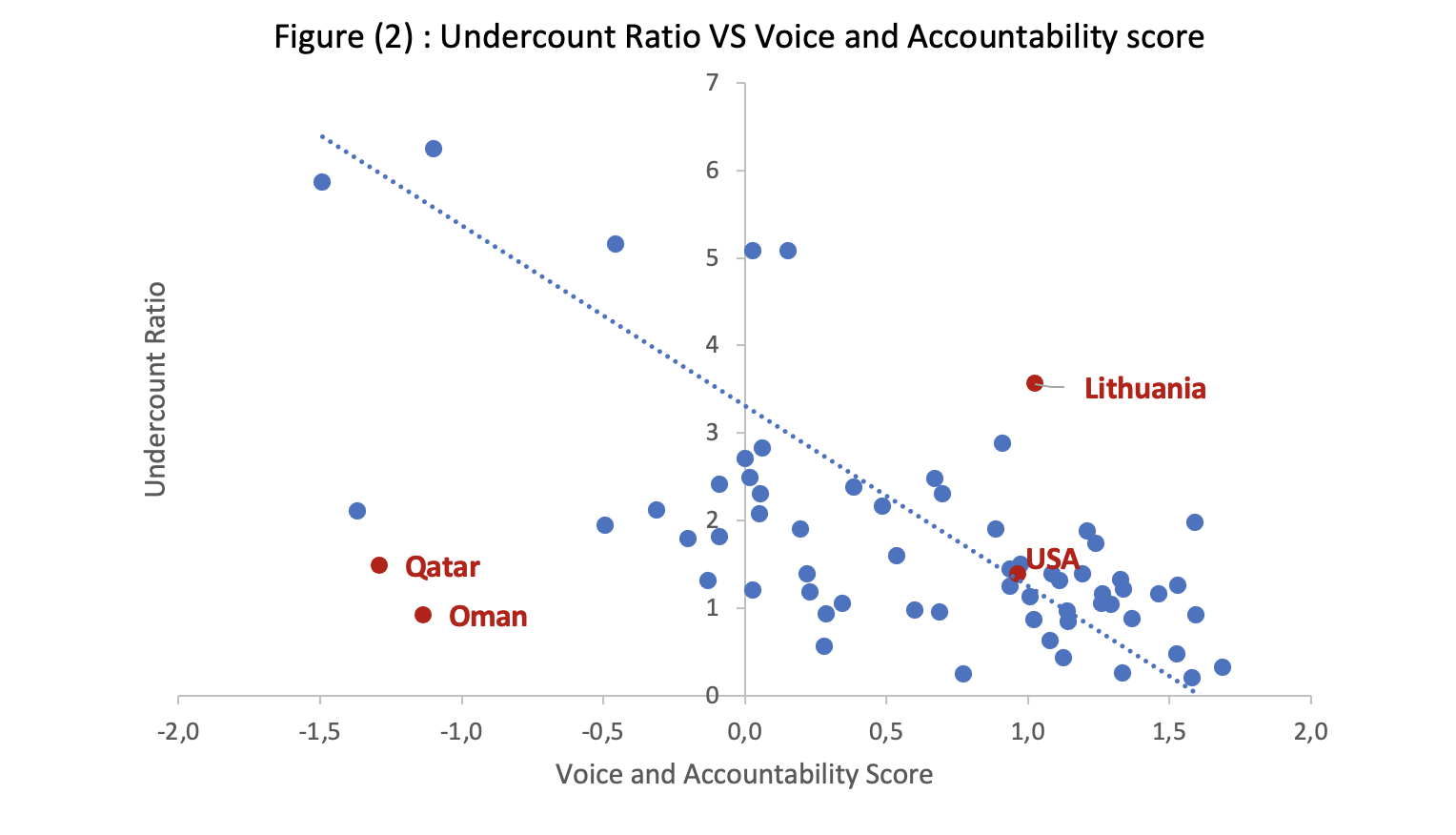
There is so much variation in the undercount ratio that if any one of the three possible explanations plays an important role, one should be able to detect their effect in the data. We ran a regression of the undercount ratio against three indicators: PPP-adjusted per-capita income, which can act as a proxy for quality of the health system and for many other possible administrative weaknesses; the data products score[3], a more direct measure of statistical performance drawn from the World Bank; and Voice and Accountability, an indicator of the robustness of representative institutions drawn from World Governance Indicators. The Voice and Accountability indicator captures citizens’ perceptions of their ability to participate in selecting their government, of freedom of expression, and of freedom of association and free media. The measure ranges from -2.5 to +2.5 across the world. In our limited sample of 71 countries, for example, Norway scores 1.7, while Belarus scores -1.4. We include this indicator to test the hypothesis that weak representative institutions, such as a vibrant opposition and an independent media, would make it easier for a government that wishes to avoid conveying bad news[4].
As the regression output shows (Table 1), only one of these variables, namely Voice and Accountability, is statistically significant at the 90% level when all three variables are included. The income and data variables are not statistically significant. Although they have the right sign, they add little to the explanatory power of the regression beyond that of the Voice and Accountability variable. When the income and data variables are dropped from the regression, the Voice and Accountability variable is significant at the 99% level.
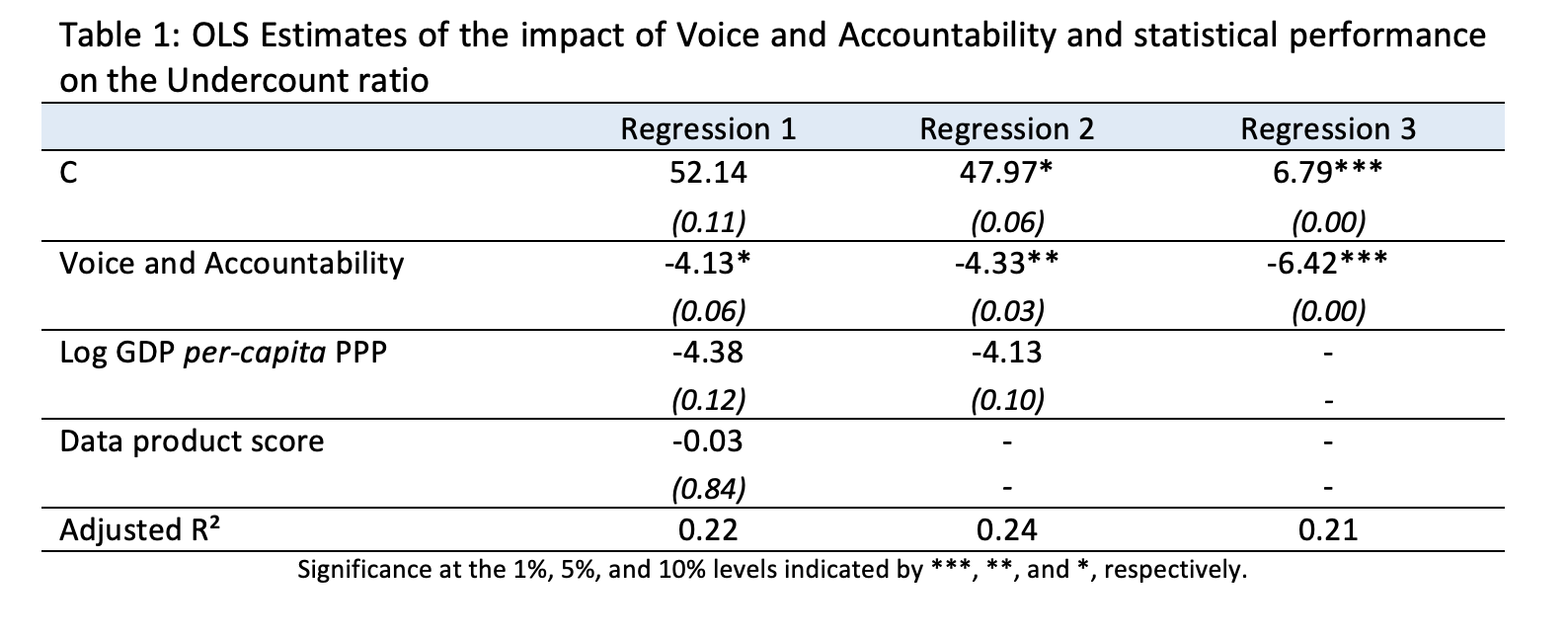
The relationship between Voice and Accountability and the undercount is also shown in the scatter diagram below, as is the regression line for Regression 1, including all three variables. Countries with the largest undercount ratios (over five times as many excess deaths as reported COVID-19 deaths) have low Voice and Accountability scores. At the other end of the spectrum, –two-thirds of countries where reported COVID-19 deaths are higher than excess deaths (an undercount ratio of less than one) have high Voice and Accountability scores, exceeding 1, which is the score of the United States. As the regression line shows, there are large deviations from this general picture. For example, Oman and Qatar, where many COVID-19 infections occurred among the guest workers that account for the bulk of the population, report more COVID-19 deaths than there are excess deaths, despite their low Voice and Accountability scores. And Lithuania, a country with a high Voice and Accountability score, reports COVID-19 deaths that are less than one-third its excess deaths.
Insofar as one can draw a policy implication about the management of pandemics from this simple exercise, it is to underscore the importance of representative institutions, including the presence of a robust and independent media, and a vibrant opposition that holds the government accountable. Accountability begins with accurate reporting, and though accurate data on COVID-19 mortality is only a first step in crafting an effective response to the COVID-19 catastrophe, it is an essential one. Another implication is that policymakers weighing the relaxation of travel rules to and from countries with weak representative institutions should treat official statistics with a double dose of caution.
The opinions expressed in this article belong to the author.
[1] Countries with undercount ratios less than 1: Denmark, South Korea, Ireland, Norway, Costa Rica, Luxembourg, Tunisia, Cyprus, France, Chile, Belgium, Oman, Sweden, Peru, Israel, Andorra and Argentina.
Countries with undercount ratios between 1 and 1.5: Aruba, Brazil, Liechtenstein, Slovenia, Canada, United Kingdom, Colombia, Montenegro, Germany, Greece, Switzerland, Kosovo, Malta, Austria, Hungary, San Marino, Spain, United States, Czech and Qatar.
Countries with undercount ratios between 1.5 and 2: Italy, Croatia, Portugal, Bosnia, Moldova, Estonia, Georgia, Latvia, Lebanon, and Finland. Countries with undercount ratios between 2 and 3: Armenia, Iran, Guatemala, Romania, Poland, Ukraine, Bulgaria, Bolivia, South Africa, Mexico, Bermuda, Ecuador, Slovakia.
Countries with undercount ratios of more than 3: Lithuania, Albania, Serbia, Kyrgyzstan, Azerbaijan, Russia, Kazakhstan, Egypt, Belarus, Uzbekistan and Tajikistan.
[2] The choice of metric also affects the count. For example, the UK ascribes to Covid-19 deaths that occur within 28 days of a positive Covid test. But some die of Covid without being tested, or – due to complications and other frailties – more than 28 days after being tested. Others may die within 28 days of a positive Covid test of other causes.
[3] To assess statistical performance, the World Bank computes a composite score based on data use, data services, data products, data sources, and data infrastructure. In our regression we used the data products score that measures whether the country is able to produce relevant indicators, primarily related to the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals.
[4] We also tried other governance indicators such as regulatory quality and government effectiveness but these were not statistically significant when we include income per capita and data products.




