Publications /
Opinion
The hike in tariffs imposed by the United States against its major trading partners since early 2018 has been unprecedented in recent history. President Trump alluded to, among others, the goal of revitalizing jobs in the country’s manufacturing industry by protecting it from unfair trade practices of other countries, particularly China. However, according to a study by two Federal Reserve Bank staff – Aaron Flaaen and Justin Pierce – released last December 23, the effect so far has been just the opposite, i.e. a reduction in U.S. manufacturing employment!
Tariff escalation – and retaliation from those affected – from 2018 onwards took place in three stages. In February of that year, surcharges were imposed on imports of washing machines and solar panels, followed in March by others affecting steel and aluminum imports. China, the European Union, Canada, and Mexico responded with retaliation on U.S. exports. A third moment came with the sequence of tariffs on imports from China announced starting in April, always accompanied by Chinese retaliatory reactions against U.S. exports.
Chart 1, taken from the Fed study, depicts the escalation of U.S. import tariffs and retaliations since 2018, including the latest rounds currently suspended after the announcement of an incoming “phase one” U.S.-China trade deal.
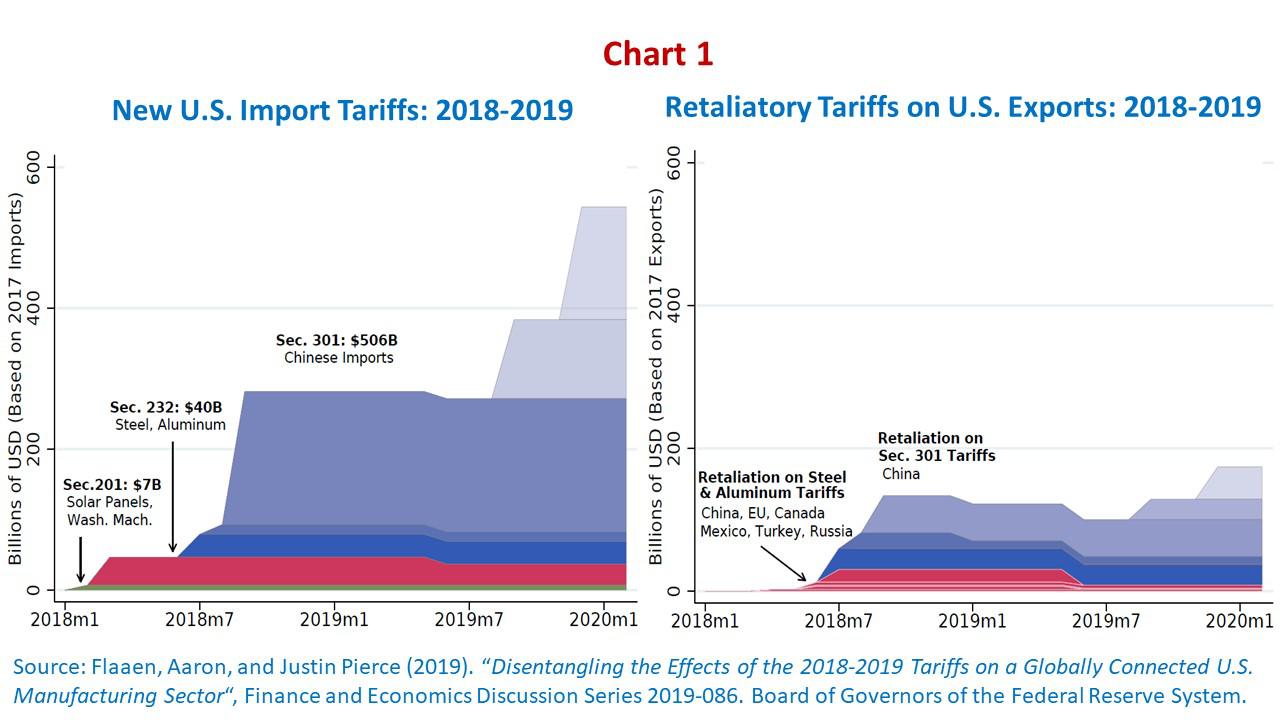
In addition to the Trump administration’s references to U.S. security issues and trade deficit reduction targets, with an emphasis on bilateral deficit cases, the resumption of domestic manufacturing employment had emerged as a promise since the electoral process. Tariffs would provide the opportunity for local production processes to take market shares occupied by foreign competitors. Higher product prices, whether imported or locally import-substituted, would be an acceptable and limited welfare cost offset by increases in manufacturing employment levels.
However, two other tariff impacts should also be considered. The imposition of tariffs on inputs and intermediate products leads to cost increases for those who use them, damaging their competitiveness domestically and externally. In addition, retaliation also affects the ability of domestic production to compete in the corresponding overseas markets.
Flaaen and Pierce estimated the weight of these effects at a very detailed sector level, namely the gain of local market shares against the burden of rising intermediate costs and overseas losses. The study comes to figures showing that the burden has outweighed the gains, with the positive contribution on employment driven by tariff protection being more than negatively offset by the impacts of rising input costs and retaliatory measures. In addition, it has led to increases in U.S. wholesale price levels.
The characteristics of industrial production as value chains integrating fragmented and geographically dispersed activities, particularly since the 1980s, explain why tariffs on specific segments end up negatively affecting a much broader set of economic activities. In addition, they tend to frustrate tariffs that are specifically set on countries of origin, on a bilateral basis: for example, much of Chinese production has moved to Vietnam, Thailand and other countries rather than to the U.S.
Is the negative effect temporary, lasting only while local production does not adjust to the new context via new investments? It should be noted that adaptation can also reinforce the negative impact sides on jobs. Therefore, there is no reason to believe that the immediate, short-term consequences of the tariff escalation would wind down over time.
The Fed study of the effects of tariff escalation did not even encompass the broader negative indirect effects, namely the depressive effect on manufacturing investments and economic growth in the U.S. and abroad generated by trade policy uncertainty, affecting particularly capital goods industries and world trade. Such an impact on investments was one of the major factors explaining the global economic growth in 2019 as the lowest since the global financial crisis.
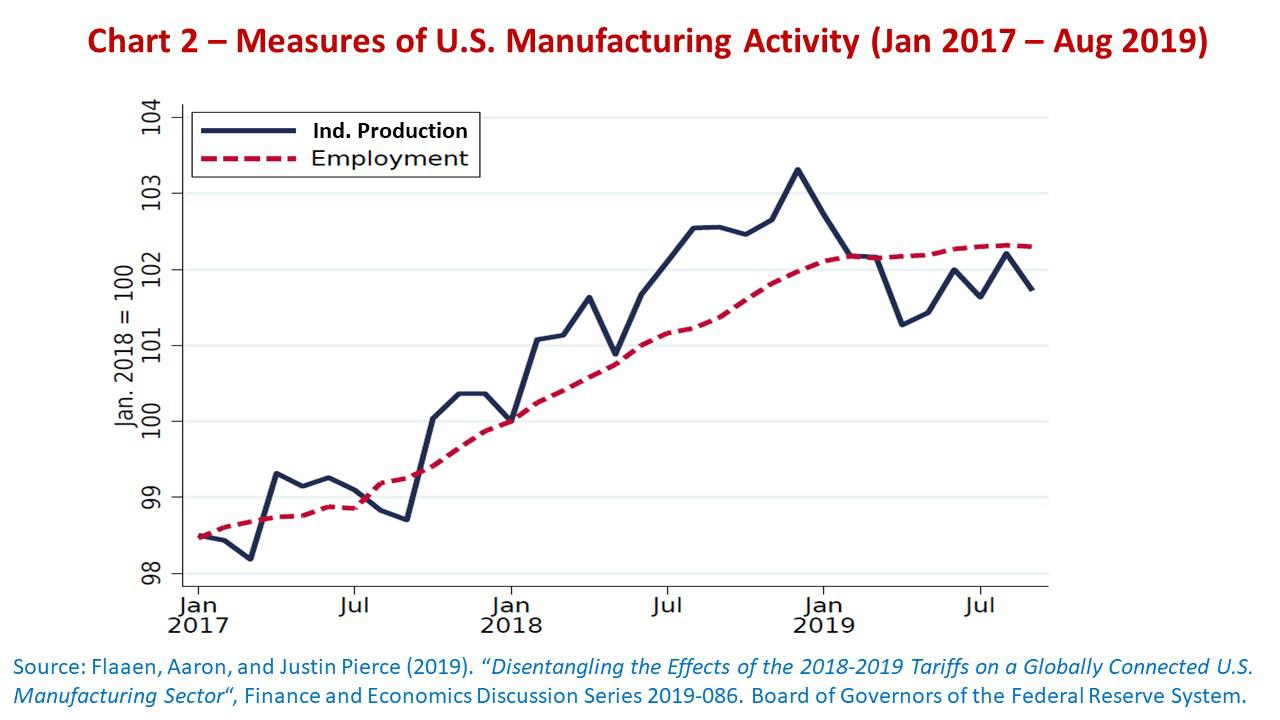
But hasn’t the U.S. GDP and employment performance remained favorable since the onset of the tariff escalation? That has occurred for other reasons, such as the fiscal stimulus provided by the tax reform of the early Trump administration, the pivotal turn of the Fed’s monetary policy, and the buoyancy of domestic consumption and services. It would have been otherwise if it had depended on the manufacturing industry – Chart 2 – and trade policy of the Trump administration.
Finally, it is worth remembering the mistake of finding it possible to shrink the U.S. current account deficit via trade measures upon countries with which it has negative bilateral balances. The current account deficit reflects the difference between domestic “absorption” (consumption and investment) and local production. In the absence of miraculous increases of the latter, the reduction of the current deficit would only occur with recession and falling domestic wages, just the opposite of the promise.







