Publications /
Opinion
The monetary policy report submitted by the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System to the U.S. Congress on Friday Feb. 19 showed that the Fed’s members have improved economic growth expectations for 2021 and 2022, expect lower unemployment rates. Meanwhile, only two of the 18 participants projected PCE (personal consumption expenditures) inflation to (slightly) exceed the 2% that serves as the longer-run objective for the monetary policy regime.
In this context, is there some justification for fears on the part of some that the $1.9 trillion fiscal package sent to Congress by the Biden government, with approval expected by mid-March, carries the risk of bringing too much stimulus to the country's economy, which is already recovering? Could the package cause inflation spikes and, consequently, a reversal of the looseness in monetary policy, with an increase in interest rates causing shocks to highly indebted non-financial companies?
There are even those who suggest the recent slight rise in longer-term interest rates on Treasury debt securities already reflect such an expectation. Last week, yields on 10-year bonds reached 1.3%, after being slightly above 0.9% at the beginning of the year. Several analysts pointed to yields implicit in 10-year protected-against-inflation government securities as embedding inflation expectations at around 2.2%, the highest since 2014. Figure 1 shows recent spikes in 5-to-10-year-forward inflation compensation.
Figure 1: 5-to-10-year-forward inflation compensation
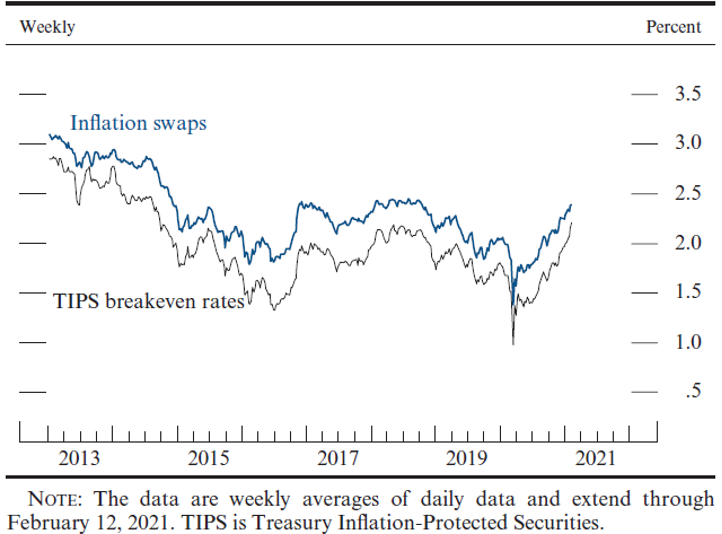
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System, February 19, 2021.
When added to previous packages since the beginning of the pandemic crisis, amounts equivalent to 13% of GDP will be reached, something unprecedented since the Second World War. It was very striking that the concern about excess has been expressed by renowned economists—including Lawrence Summers and Olivier Blanchard—who have always called for fiscal policies to not leave the task of recovery entirely on the shoulders of monetary policy.
Even before considering the Biden package, the U.S. Congressional Budget Office had already projected the country's GDP as exceeding the pre-pandemic level this summer. If the Trump administration's second package was enough, the impact of the Biden package on demand (9% of GDP) would be beyond what is necessary for the return to potential GDP. Morgan Stanley Research has forecast a 6.5% GDP growth rate for 2021 and a trajectory even above the pre-COVID-19 path (Figure 2).
Figure 2 – US real GDP (rebased Q4 2019 = 100)
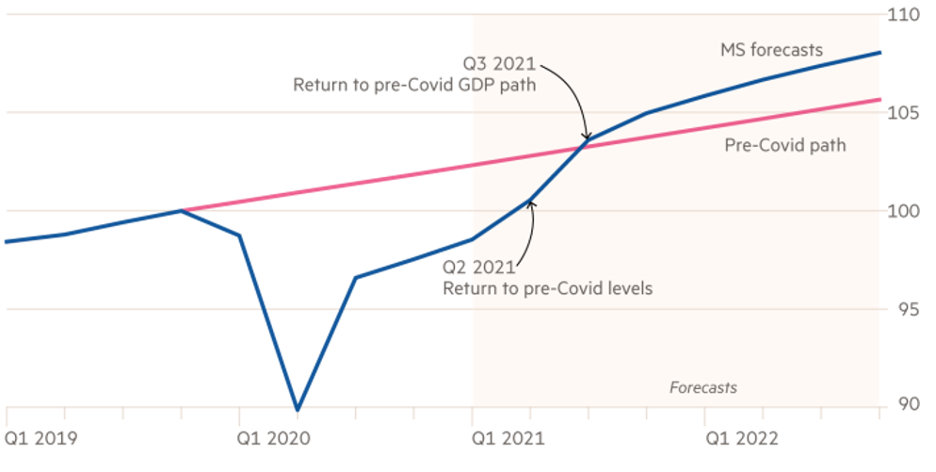
Source: Gille, C., Financial Times, February 18, 2021.
The fiscal package has components that need to be differentiated. On the one hand, it would provide an amount of resources that could be considered as part of the extraordinary public expenditure related to the pandemic, and which does not correspond to a macroeconomic recovery policy, even though it will have an impact on aggregate demand. This includes money to speed up the vaccination campaign, including spending by subnational entities, and reinforcement of unemployment insurance. On the other hand, items pointed out as excessive and poorly focused include another round of checks sent directly to households, as was done last year.
Paul Krugman, for his part, has expressed less concern about the potential excess aggregate demand that would be be brought about by such checks, which would not be focused on the lower levels of the income pyramid, judging by their diversion to precautionary savings by households last year. Former U.S. Treasury Secretary Larry Summers reiterated that, even if this is the case, the corresponding fiscal space should have been reserved for some future package that is expected to come for investments in infrastructure and “green recovery“.
However, two relevant aspects must be taken into account. First, according to Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen, it would be better to run the risk of excess than insufficiency.
In addition, the Federal Reserve's new monetary policy regime puts the 2% inflation target as an average, not as a ceiling forcing monetary policy to act to prevent it in advance. After a long period of inflation below 2%, even in years with low unemployment and interest rates on the floor, monetary authorities can afford to wait some time with above-average inflation until they are compelled to pull the brake. The report presented to Congress Feb. 19 says this explicitly.




