Publications /
Opinion
Data recently released on the first-quarter global domestic product (GDP) performance of major economies have showed how significant the impact of COVID-19 has been on economic activity and jobs, with large contractions across the board. The ongoing global recession is poised to be worse than the “great recession” after the 2008-09 global financial crisis, especially from the standpoint of emerging market and developing economies. The depth and speed of the GDP decline will rival that of the Great Depression of the 1930s.
But how swiftly will national economies recover once the pandemic has passed? And when will that happen? That will depend on how successful the containment of coronavirus and exit strategies will be, as well as on how cost-effective will be the policies designed to deal with the negative economic effects of coronavirus.
Coronavirus has taken down global economic giants
The U.S. real GDP contracted at a seasonally adjusted annual rate (saar) of 4.8% in the first quarter of the year, the worst outcome since the last quarter of 2008. The second quarter is likely to come even worse, with forecasts pointing to a real GDP decline around 40% saar. These are figures not seen since the Great Depression of last century. More than 20 million U.S. workers lost their jobs in April and the unemployment rate reached levels as high as 14.7%.
The Euro Area is another fallen giant. In the first quarter of 2020, its GDP shrank 14.4% q/q saar, as lockdowns were imposed around mid-March and activity started to run about a third below normal levels. The level of activity may have bottomed last month, assuming that restrictions will be gradually eased in the following weeks. In any case, forecasts point to a 45% annualized rate of GDP drop in the first half of the year.
Japan’s real GDP is forecast to decline by more than 40% saar in the second quarter. Daily increases in the number of infections led the government to prolong the state of emergency for an additional month after May 6th.
China, in turn, suffered first an outbreak-induced sudden stop in February (Canuto, 2020a). There was a rebound in March but not enough to allow a return to previous GDP levels, with manufacturing prospects worsening a bit last month. The normalization of domestic consumer demand and the service sector has been a key driver of China’s economic recovery in the second quarter, but demand conditions have not been much supportive. The plunge in exports last month reflects the global nature of the crisis and expresses the limits of any isolated country recovery, while slump remains underway elsewhere. Domestically, it is worth noticing the hesitancy to consume services even as quarantines were lifted.
The wide variation in first-quarter annual rates of GDP negative outcomes among the giants – U.S (4.9%), Euro area (14.4%), and China (34.7%) – can be associated to their different timings of COVID-19 outbreaks. But they will all have crossed a rough patch at the end of the semester.
The depth and severity of the crisis were displayed in the IMF World Economic Outlook forecasts released in mid-April (IMF, 2020). The IMF expects the global GDP per capita to shrink by 4.2% this year, while it declined by 1.6% in 2009, during the global financial crisis (Figure 1). 90% of all countries are poised to exhibit negative GDP growth this year.
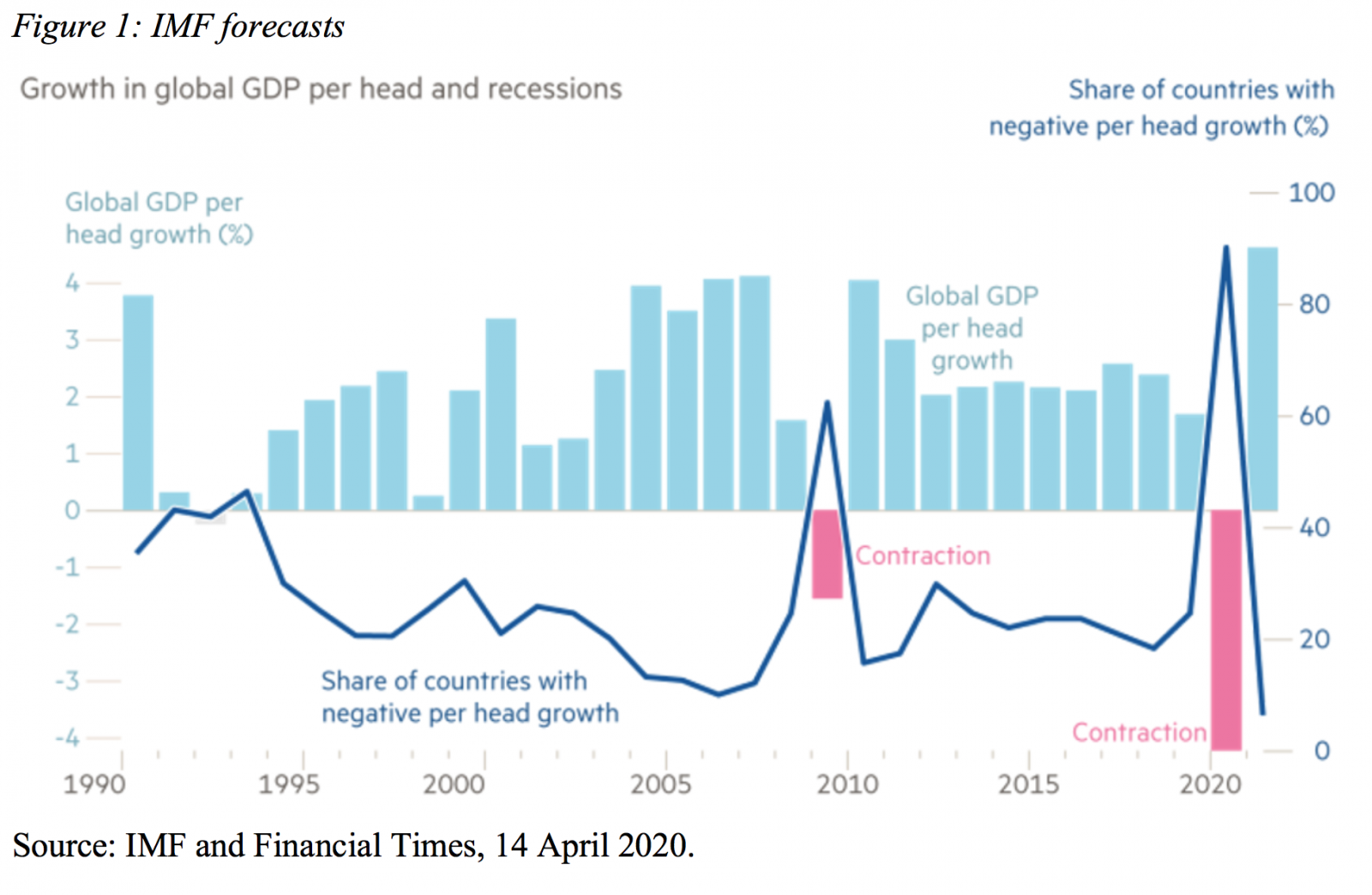
The recovery along 2021 is not expected to be enough to compensate for the ongoing GDP declines and GDP per capita in advanced economies at the end of next year is likely to still be lower than December 2019. Emerging market and developing economies, in turn, are facing a “perfect storm” and, in most cases, performance will be even gloomier (Canuto, 2020b).
How shaped will the economic recovery be?
A post-crisis recovery is expected to begin in the second half of the year, at least in those countries where the coronavirus outbreak may be considered to be past and policies to flatten the pandemic curve can be relaxed (Canuto, 2020c). The shocks caused by Covid-19 have been profound while they last but will invariably be temporary.
How fast will this recovery be, i.e. what will be the country-specific shape of the GDP evolution curve over time? What will this format depend on?
Let us mention four possible stylized formats for such GDP evolution, taken from “the ABCs of the post-COVID economic recovery” outlined by Louise Sheiner and Kadija Yilla (2020). The most optimistic is that of a "V" (Figure 2). After suffering a strong blow during the pandemic, the economy soon returns to its previous trajectory. The loss of GDP during the period of restrictions - due to supply shocks and pent-up demand - is definitive. However, if there are no lasting consequences of the virus outbreak period and the corresponding economic downfall on the production system and on economic agents’ conditions, everything returns to the previous normal.
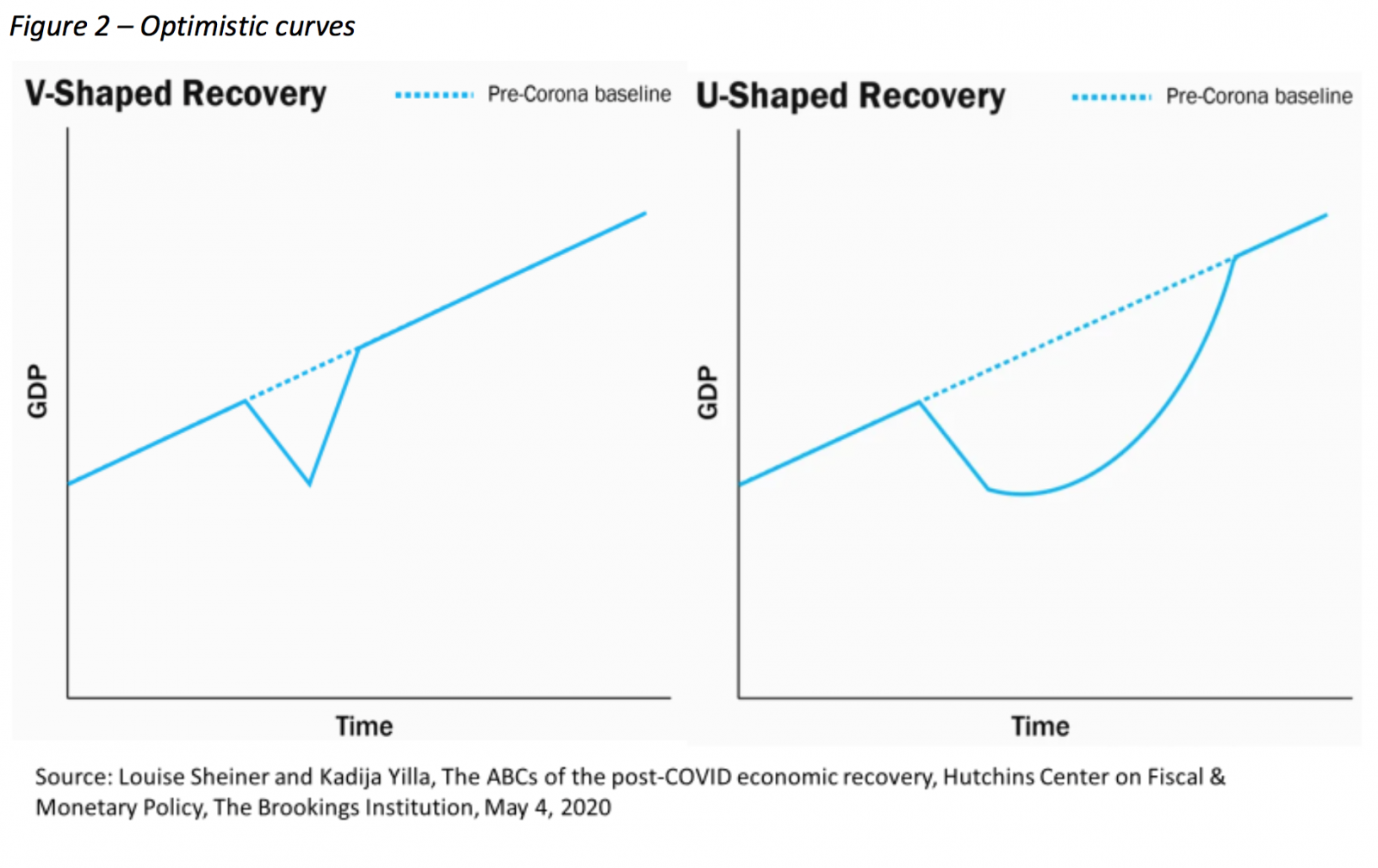
Something less optimistic and more likely than the previous one is the “U” shape (Figure 2). The effects of the pandemic persist, not least because the norms of social distance remain for some time, but eventually GDP returns to its previous trajectory after a period of decline. Even if sanitary conditions are declared to be normalized, consumers and companies will hesitate before returning to their previous consumption patterns and investment plans.
There are, however, two other more pessimistic trajectories. One is the shape of a "W" (Figure 3). This will be the case if, after a relaxation of “social distancing policies”, new outbreaks of COVID-19 appear, and new rounds of these policies are implemented. This possibility is mentioned by all those who alert against any early lifting of restrictions on mobility and crowding.
Finally, there is a possibility that the damage left by the new coronavirus is permanent or durable. In this case, the recovery takes the form of an "L" (Figure 3). The economy grows again, but at lower levels of GDP over time than would be the case if COVID-19 had not appeared.
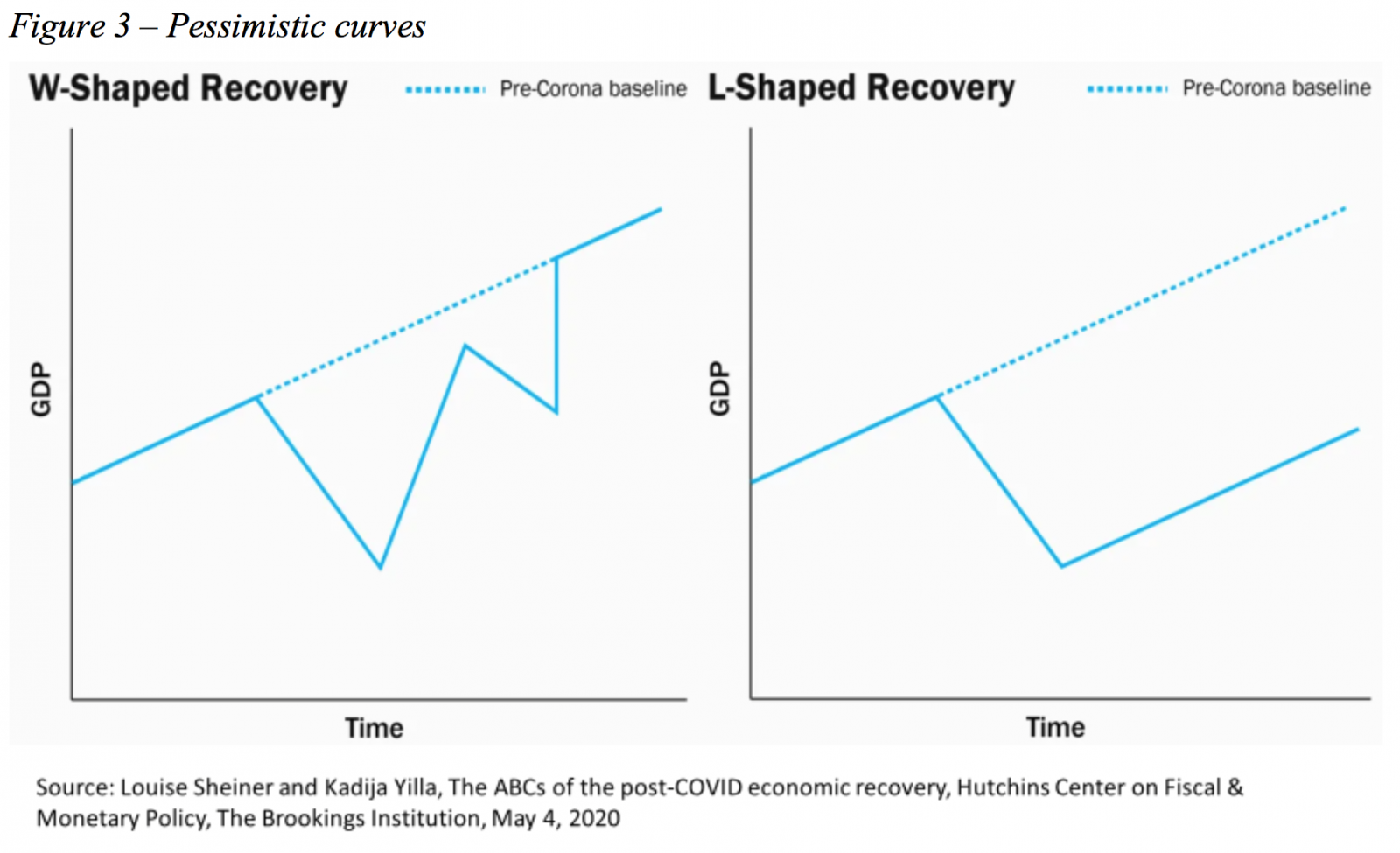
Previous investment plans can be shelved. Previously healthy companies may have gone bankrupt due to the abrupt and sudden deterioration in their operating conditions during the crisis. Changes in the pattern of consumption can lead to the permanent elimination of jobs without unemployed workers finding jobs quickly elsewhere. Production processes can be changed to less efficient ways to avoid risks previously not considered relevant. Net worth conditions of families, firms and the government may also suffer significant deterioration during the epidemic.
Certainly, public debt is rising worldwide, something naturally expected as a result of the state's role as the ultimate catastrophe insurer in all countries of the world. Emergency and temporary measures, financed by the public sector, have generally been adopted, aiming to minimize the disastrous consequences of the - temporary but potentially lethal - sudden stop caused by the coronavirus. Not by chance, around the world, governments have announced dramatic income transfer policies for informal workers, boosts to unemployment insurance, special lines of credit for business segments - sometimes tied to job preservation -, tax relief measures and so on.
Strictly speaking, the shape of the recovery will depend on the quality - in terms of cost-effectiveness - of those public policies. On the one hand, there is the burden of public debt. On the other hand, the greater the smoothing of household income streams - especially the most vulnerable and without accumulated savings - and the lower the wave of bankruptcy of healthy businesses under normal conditions, the closer the country will be to the "U" shape than to the "L".
The shape of GDP evolution will also depend on whether previous financial/fiscal fragilities and vulnerabilities are aggravated by the coronavirus-related crisis. Finally, as we noticed in the case of China, global interdependence means that what happens elsewhere also matters locally.
As COVID-19 outbreaks are still unfolding in most places in the world, it is still early to bet on any specific shape of recovery as predominant anywhere.




