Publications /
Opinion
As the world is shifting away from conventional fossil fuels towards renewable energy sources, the power industry is starting to invest more in sustainable clean energy installations rather than the traditional large-scale infrastructures, which rely mainly on oil and coal.
Besides its environmental benefits, this shift to renewables is very likely to benefit economic growth as well. A recent study of the International Renewable Energy Agency shows that, indeed, doubling the share of renewables in the energy mix by 2030 would lead to a rise of global Gross Domestic Product (GDP) up to 1.1 percent. It would also improve global welfare by 3.7 per cent and support the creation of over 24 million jobs in the sector all over the world.
In order to achieve these goals, digitalization is considered as a key factor. According to the International Energy Agency, digitalization - described as “the growing application of information and communications technologies (ICT) across the economy”- is set to make energy systems, particularly power generation systems, more safe, productive, accessible and sustainable.
The pace of digitalization in energy is increasing rapidly. Between 2014 and 2016, global investment in digital electricity infrastructure and software increased over 20% annually, exceeding investment in gas-fired power generation (Figure 1).
Figure 1 : Investments in digital electricity infrastructure and software
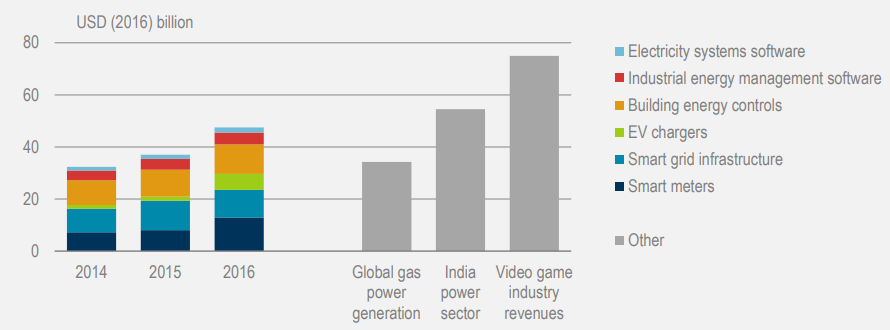
Note: Global gas power generation and India power sector are 2016 investments; EV = electric vehicle.
Source: Calculations for investment in digital infrastructure and software based on Markets and Markets (2016), Internet of Things in Utility Market; BNEF (2016), Digital Energy Market Outlook.
The rise of digitalization is driven by numerous factors such as automated metering, grid decentralization and growth in distributed generation. It is also enabled by significant advances in data, analytics and connectivity. Therefore, digitalization of energy systems enables utilities to maintain grid stability and reliability, monitor the grid and identify points of failures, reduce operations and maintenance costs, optimize and forecast energy production and extend the operational lifetime of assets (Bloomberg, 2017).
Can digitalization be the solution for Africa’s power deficit?
In the past ten years, African countries have witnessed substantial economic growth, coupled with an increase in population and the emergence of a wider middle class. This has led to a greater energy demand in a continent that is constantly facing energy challenges.
The first challenge concerns the low electrification rates. The picture is not all dark however. Access to electricity, in sub-Saharan Africa particularly, has improved throughout the years, as seen in countries like Côte d’Ivoire, Ethiopia, Ghana and Kenya. The pace of electrification has almost tripled between the years 2000 and 2012, and in 2014, electrification efforts surpassed population growth for the first time.
Yet, 590 million people, roughly half of Africa’s population, still do not have access to electricity, “making it the largest concentration of people in the world without electricity access,” as explained by the International Energy Agency (Figure 2). In addition, the electrification rate stands at only 43%. These contrasting trends reflect the two-speed growth that the continent is facing in the energy sector.
Figure 2: Population without access to electricity by region and installed power generation capacity in sub-Saharan Africa by fuel
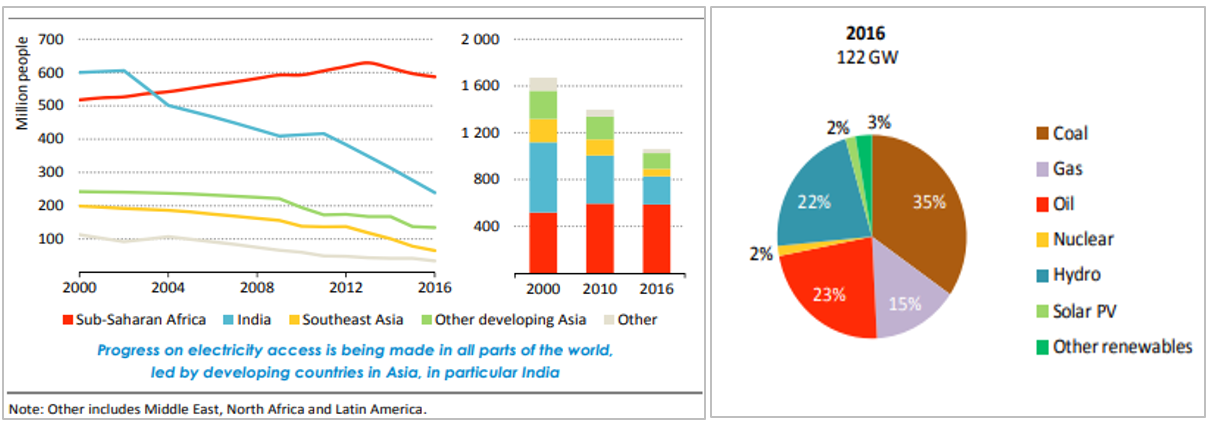
Source: International Energy Agency, 2017.
The second challenge is overcoming Africa’s strong reliance on fossil fuels. Nearly three quarters of today’s total installed generation capacity of 122 gigawatts (GW) in Africa originates from fossil fuels, with coal representing 35%. Renewables, on the other hand, dominated by large-scale hydropower, make up about a quarter of the total capacity (Figure 2).
The use of renewables, particularly wind power and solar photovoltaic (PV) technology, is likely to increase in the upcoming years as the cost of renewable energy technology is decreasing, while renewable energy continues gaining further attractiveness as a more sustainable alternative. Therefore, adapting Africa’s power systems to accommodate new sources of electricity-generation becomes a necessity.
From this perspective, digitalization and smart technology are seen as innovative solutions to address Africa’s electricity issues. In fact, as decarbonization, decentralization and digitalization are expected to drive the transformation of the African energy sector, new opportunities are emerging to help carry efficient, affordable and reliable electricity to consumers (GE Power, 2018).
Smart decentralized grids for instance can help develop Africa’s energy capabilities while ensuring the security of supply. Indeed, grid expansion continues to be the essential mean of introducing electricity in the region. Yet, conventional grids are typically characterized by partial control, poor technology integration and optimization, and fragility of systems. Therefore, decentralized systems can help tackle those issues- particularly in land areas not yet reached or too expensive to electrify by grid connection- by:
- Increasing grid flexibility as they provide multiple opportunities for automation at any point of the value chain;
- Better managing the electricity flow through two-way digital communication and control capabilities;
- Improving preventive maintenance through the use of smart sensors;
- Improving cyber security through improved resilience to cyber-attacks on the grid;
- Facilitating smooth integration of renewable energy sources.
Figure 3: Key impact areas of digital grids
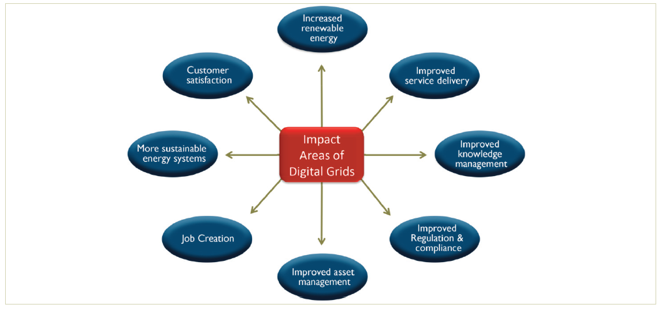
Source: GE Power, 2018.
Information Communication Technology Integration is another promising area concerning the use of digitalization in Africa’s power sector. It can allow stakeholders to manage grids efficiently through real-time or deferred data transmission and increased speed and volume of data output. As a result, utilities would be able to maximize cost reduction and increase power reliability, thus also increasing customer satisfaction.
Transferring the information is not enough if it is not monitored. Thus, for this particular need, digitalization proposes a wide area monitoring and control systems that enable power systems to observe the performance of grid components. This paves the way for important cost-saving benefits associated with predictive maintenance and self-diagnosis.
In addition, other products of digitalization such as intelligent electronic devices, advanced metering infrastructure, and grid automation can help Africa ensure a smooth integration of renewable generation, allowing the continent to tap into its potential for renewables. It can also help predict maintenance in distributed grids in order to reduce outages, which is another area of weakness in Africa’s power systems (GE Power, 2018).
In order to implement these new technologies to the power sector, Africa needs to initiate a cultural shift towards an information-based digital economy. It also needs to transition from traditional business models, which calls for considerable investment in physical assets.
Technology cannot solve all of Africa’s problems, but it can help with many.








