Publications /
Opinion
While the economic recovery around the world remains uneven, fragile, and unbalanced across sectors, financial markets are generally doing very well, thanks! In the United States, only half of the unemployment caused by the pandemic last year has been reversed, while stock markets continued to boom. Of course, this largely reflected the extraordinary support given by monetary authorities since March last year.
As in the period after the 2007-08 global financial crisis, voices have been raised talking about monetary policy and central banks as drivers of income and wealth inequality. The unconventional policies of “quantitative easing” protect the holders of financial assets and value their properties, while workers cross a rough patch on the real side of the economy. As we have already discussed here, financial markets have disconnected from hardships in the street of commons, with the help of the policies of monetary authorities.
Does it make sense to assign an impact of concentration of income and wealth to central bankers' policies? It's complicated...
The argument about central banks’ unconventional monetary policies worsening inequality typically begins with the remark that monetary easing acts in part by raising asset prices, like stock prices. As the rich own more assets than the poor and middle class, “quantitative easing (QE)” policies would increase already high disparities of wealth in countries where they have been applied.
However, first consider that volatility and below-potential macroeconomic performance particularly affect the bottom of the income and wealth pyramids. Adequate fulfillment of the stabilizing function attributed to central banks is good for those who have less capacity to defend themselves against unemployment and inflation.
To those who always ask me about rescuing or supporting financial institutions in crisis situations, I always ask back about what the alternative scenario would be. The design of such support can always minimize the rewards in terms of wealth of owners, but the truth is that macroeconomic scenarios in cases where the financial system collapses cannot be out of sight, as economic recovery gets harder under such circumstances.
Mary Daily, president of the Federal Reserve Bank of San Francisco, recently observed how the long expansion of the United States economy after the global financial crisis could only happen because of the stabilization measures that followed, with interest rates decided on the basis of a return of inflation to the 2% per year target. Unemployment rates fell to levels close to historical lows. The country's average GDP growth rate in the period fell short of previous decades, but this was not due to monetary policy. She notes:
“This created real opportunities for a large number of sidelined Americans, many of whom were thought to be permanently out of the labor force or lacking the right skills to work in an evolving job market. (…) By early 2019, employers were hiring African American and Hispanic workers at rates equal to or higher than those of white workers. (…) This reduced long-standing unemployment gaps, narrowing them to historic lows.”
In addition, according to a recent Federal Reserve Bank bulletin, the prolonged macroeconomic expansion particularly valued the assets held by those at the bottom of the wealth pyramid (Bhutta et al, 2020). Figure 1 shows how the U.S. median family net worth kept climbing from 2013 to 2019, while the mean family net worth exhibited a lower performance. Median measures divide the population in two halves and are lower than means because of the degrees of wealth concentration at the top. A rising median relative to the mean therefore means that the net worth of families at the lower part of the pyramid grew more.
Figure 1 - Change in median and mean family net worth, 2013–19 surveys
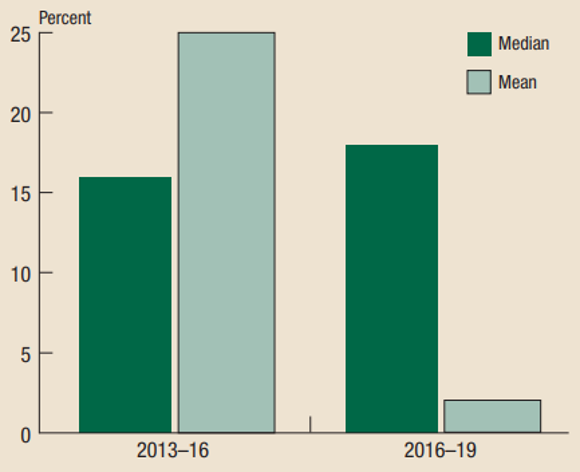
Source: Bhutta et al (2020)
There are those economists who do not recognize the need for macroeconomic stabilization through proactive central banks and argue that loose monetary policies favor the top of the pyramid. This would be the case if expansionist policies favored profits more than wages, in addition to the extraordinary gains of the financial intermediaries used to implement the policies (Weiss, 2019). Empirical evidence, however, points to the predominance of distributional effects on income from expansionary monetary policies (Colbion et al, 2014). Across business cycles, monetary policy effects do not tend to make much of a net effect on overall inequality (Bernanke, 2015).
If, on the one hand, it does not seem appropriate to say that stabilization policies by central banks increase inequality, on the other it is increasingly recognized how inequality in income and wealth affects the effectiveness of their policies. As Luiz Awazu Pereira da Silva, Deputy General Manager of the Bank for International Settlements recently noted (BIS, 2021):
“…inequality reduces the effectiveness of monetary policy transmission. (…) . High income concentration can indeed affect the transmission of monetary policy through the different effects easy monetary conditions have across heterogeneous households. Wealthier households have a much lower propensity to consume; hence their consumption may be less reactive to monetary stimulus. In turn, poorer households may not benefit from easier credit conditions because they lack collateral or adequate credit scores and are hence unable to borrow.”
The heterogeneity of monetary policy effects on heterogeneous household conditions is illustrated in Figure 2, taken from a speech by Philip R. Lane, member of the Executive Board of the ECB. It displays how the overall effect on consumer spending through various transmission channels of a 100-basis point cut in eurozone interest rates varies according to household wealth. As Lane (2019) explains:
“First, the standard, intertemporal substitution channel is present only for financially-unconstrained households which are able to save. It makes up only about a third of the total impact on aggregate consumption. Second, the cash-flow channel is particularly strong for homeowners with limited financial assets, who tend to have large mortgages, often with adjustable rates. Third, spending is substantially stimulated via the income channel. This channel is heavily skewed towards lower-income households, who also tend to benefit disproportionately from a stronger labor market. Fourth, the strongest asset price effect occurs through the increases in house prices. This effect turns out to be quite large for highly leveraged homeowners, since their consumption is more sensitive to house prices.”
Figure 2 - Effects of a 100-basis point cut in interest rates on consumption in the euro area, depending on household wealth
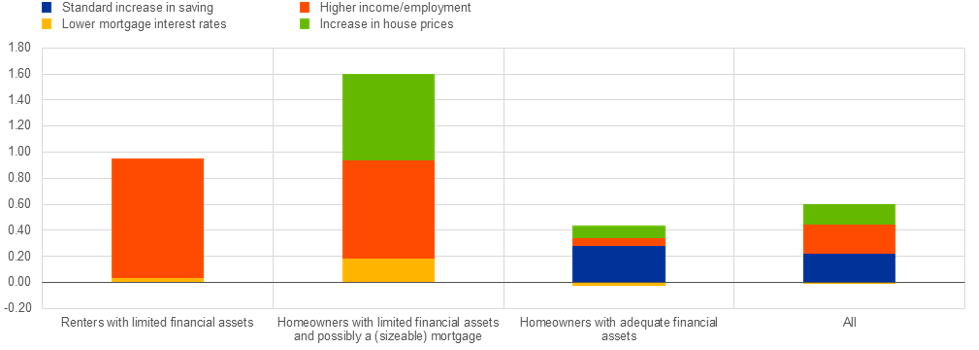
Notes: The figure shows a decomposition of the effects of a 100-basis point cut in interest rates on consumption. The total consists of four parts. The standard intertemporal substitution effect (IES), the cash-flow effect, the income effect, and the housing wealth effect. The size of these effects varies depending on households’ wealth. Euro area in this chart refers to France, Germany, Italy, and Spain.
Source: Lane (2019).
Consumption spending of the lower-income cohort and the cohort of homeowners with only limited financial assets rises more intensively as a result of a 100-basis point cut in interest rates, moving up by almost 1.0 percent and 1.6 percent respectively, while consumption of the financially unconstrained group increases only by 0.4 percent. The bottom-line is that the effects of monetary policy decisions depend on the profile of income and wealth distributions.
The rise in income and wealth inequality in recent history in many countries has fundamental, structural reasons, such as technological changes and the impacts of globalization, in addition to the absence of effective social protection networks and national traits regarding race bias, ethnicity, gender, and social classes in access to education, jobs and sources of income. Tax and public spending policies can do a lot about it. Financial regulators can also help through actions and regulations that democratize access and availability of financial resources at low cost, minimizing market concentration.
In principle, it would be up to monetary policy to avoid unemployment and inflation, as in inflation targeting regimes adopted by independent central banks. It should be noted, on the other hand, that recent developments in central bank policies, going beyond controlling short-term interest rates and avoiding the illiquidity of longer-term assets, tend to blur the borders between monetary and fiscal policies, due to the selectivity over what assets to favor.
In this context, there are even proposals for coordination between fiscal and monetary policies to define fiscal programs to be supported via monetization by the central bank (Bartsch et alii, 2019). There is also the proposal by Christine Lagarde, president of the European Central Bank, to grant special treatment to “green bonds” in their asset acquisition programs, making “quantitative easing (QE, in English)” a “quantitative greening”. Like the climate agenda, fiscal programs dealing with inequality may well end up falling into the central bank arena!
The opinions expressed in this article belong to the author.





