Publications /
Opinion
Over the next couple of months, we want to explore the investing climate in Sub Saharan Africa (“SSA”) and try to understand where it is and what elements/variables are required to increase the continent’s attractiveness to institutional investors and thereby speed up the continent’s development. We will discuss the Private Equity industry in Africa and delve into the challenges faces. We will then work through how best to address them, and in particular, in the Agribusiness sector.
The investing world’s interest in Africa has been increasing for some time. Africa chatter among institutional investors is on the rise; wherever one looks, The Economist, the FT, the Wall Street Journal, Le Monde and many others are writing about Africa as an investment destination and creating Africa portals for interested parties. For many investors, it is a region that has never been on their radar screens due to perceived risk, mainly political risk, and the lack of purchasing power on the continent. Now they are being forced to consider it because of the continent’s growth profile relative to other investment destinations. However, investors remain hesitant to commit capital to the continent. Non-DFI institutional investors really do not know how to frame an investment proposition. What is clear to all, however, is that the capital needed to fuel Africa’s growth potential has to come from private equity capital. The main reason for this is that international corporate investors are not qualified to institutionalize the target companies on the continent, hence the opportunity for Private Equity.
However, capital formation for Private Equity firms with Africa strategies remains slow. Why?
In general, Investors invest in stable structures/environments where the risks can be quantified and managed. Good investors invest only when the reasons not to invest have been removed.
This Venn diagram summarizes how an investor might begin to screen investment opportunities in SSA.
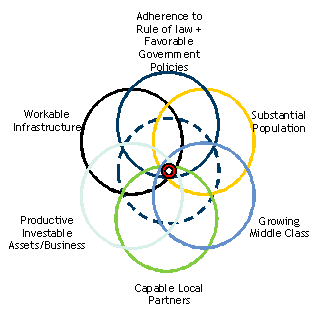
It is important to remember SSA is not a single investment destination. There are many jurisdictions within it. This model helps an investor narrow the region’s opportunities into a manageable and actionable opportunity set. Let us review these variables.
Each time I travel to the continent, I am shocked by the purchasing power evident on the continent. The continent’s population growth and the size of the emerging middle class is visible for all to see. The only challenge for investors is the “visibility” of the purchasing power. Substantial amounts of the population’s money remains outside the banking system – off the grid so to speak. For the uninitiated Africa investor, this is something that must be proven by other means. For those of us from the continent we see it in other ways, e.g. the market price per m2 in the main shopping districts of the major cities, among other indicators.
This actually helps make an important point that is common to all frontier/emerging markets. Information and data, be it for market data, or individual financial statements, needs to be extracted by interpolating different adjacent sources of data, and the conclusions synthesized, as most of the raw data is not sufficient for the first world investor. Many walk away saying it is too messy and that it is an indication of the risk.
The continent has invested heavily in its infrastructure to bring it to ‘workable’ standards. This does not mean more can not be done. In the Agribusiness sector, government infrastructure investing is a public good and a catalyst to Private Equity investing in the sector, and ultimately the development of the sector. However, enough is there for investors to work with. It is within this framework that the local families and entrepreneurs have built their businesses. When we investigate how investors should look at investing in the Agribusiness sector in a later installment, we will look more closely at the difference between public goods investing and private capital investing in infrastructure.
What is clear, however, is that the majority of the potential target businesses are what one would call distressed in some way; under capitalized, with capital structures that stress the operational efficiency of the business and under-managed with bad systems. Yet the businesses lumber along. The owners and operators do not know how to seek help or partners, and the service industries to help these businesses are under developed or largely non-existent. What is on the market is not necessarily what an investor would want. This is a long way of saying that George Akerloff’s Lemon Theory is alive and well in Africa; the best opportunities need to be unearthed by closing the information asymmetry.
This leaves the final two variables:
1- Adherence to the rule of law and favorable government policies, and
2- Capable Local Partners
Institutional investors and their partners (the Private Equity firms) do not know how to find a good local partner who can help them understand and become comfortable with the legal framework, investor protection laws and who are, or can become, good investors/operators in their own right. Suffice to say, applying existing frameworks in the US or Europe will not work. Institutional investors must also invest in these relationships and educate their chosen partners in the values and processes that make a good investor. There is no silver bullet, but time and effort that will lead to the establishment of successful investing platforms. This process has already started, but there are not enough such platforms to meet the needs of the African opportunity/continent’s need for capital as a whole. The real question is how should institutional investors go about looking for the best partners to help them make successful investments in Africa; fundamentally, what are the variables required for building successful investment platforms in Africa? We shall visit this very question in the next installment.






