Publications /
Opinion
The Policy Center for the New South and the Economic Research Forum held on March 20 a workshop titled ‘Stabilization and adjustment towards inclusive and sustainable policies in MENA: The Moroccan case study’. The event took place at the PCNS headquarters in Rabat, Morocco. It brought together renowned Moroccan economists and scholars to discuss the issue of public debt sustainability in the context of the Moroccan economy. It was an occasion to revisit the main features of the Moroccan economy over the last two decades, and to discuss the recent outlook and what it implies for the future trajectory of public debt.
Economic Growth in Morocco: A Change of Regime in the Last Decade
Thanks to a strong push for capital accumulation in the early 2000s, as exemplified by a series of sectoral policies aimed at building modern basic infrastructure and introducing new industrial lines, and a proactive policy of openness, the Moroccan economy has performed solidly, with an average non-agricultural GDP growth rate of 4.5%, between 2000 and 2012. However, this model has reached its limits. Since 2013, the average growth rate has dropped by an average of 1.5 percentage points. This change was driven by the lower contribution of investment to economic growth, as exemplified by a sharp fall in the incremental capital-output ratio due to a fall in total factor productivity (TFP) growth, and, to a lesser extent, the fall in international demand in the aftermath of the Great Recession and the euro debt crisis.
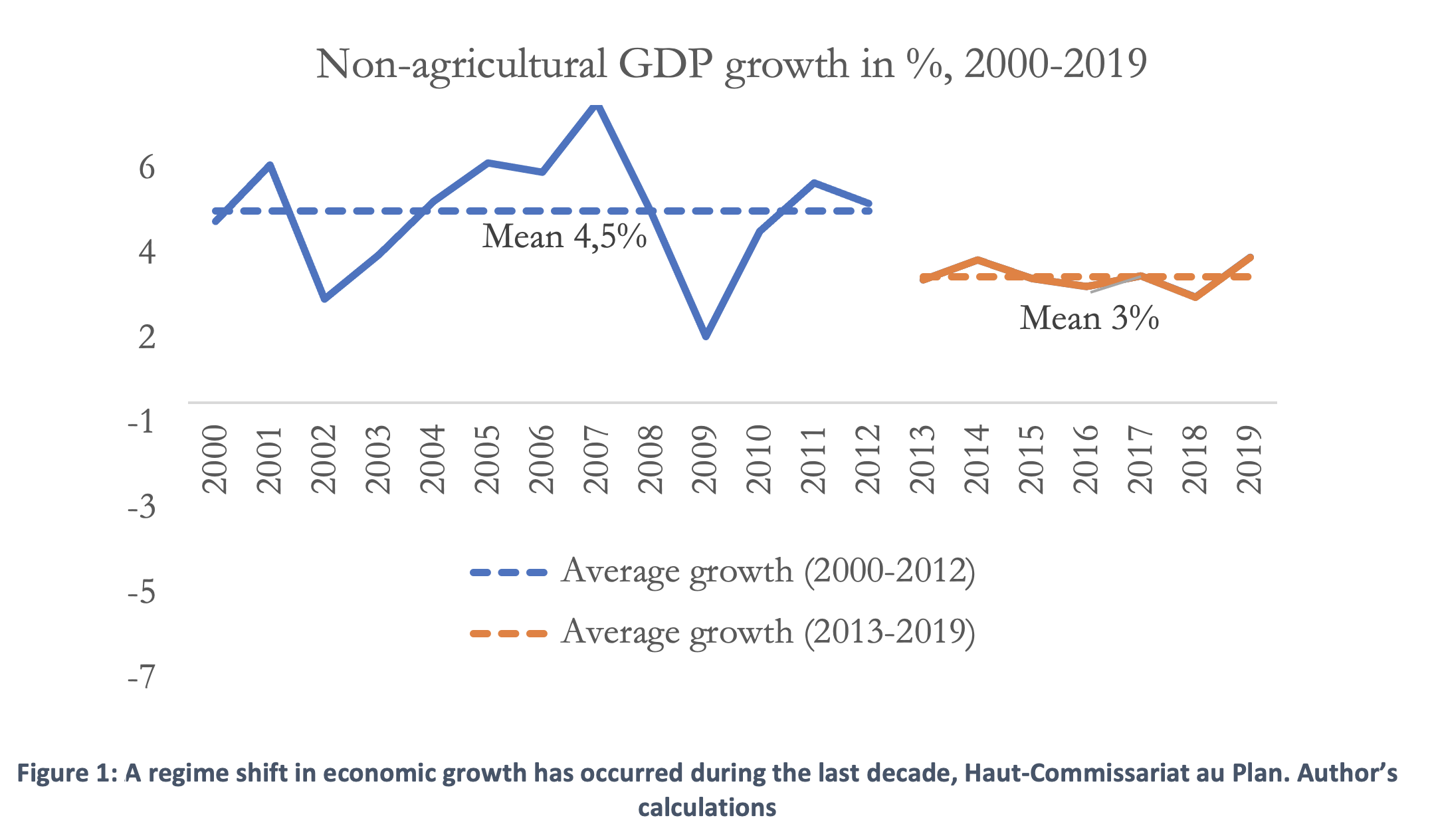
The Moroccan economy has performed during the last two decades within under a stable macroeconomic framework
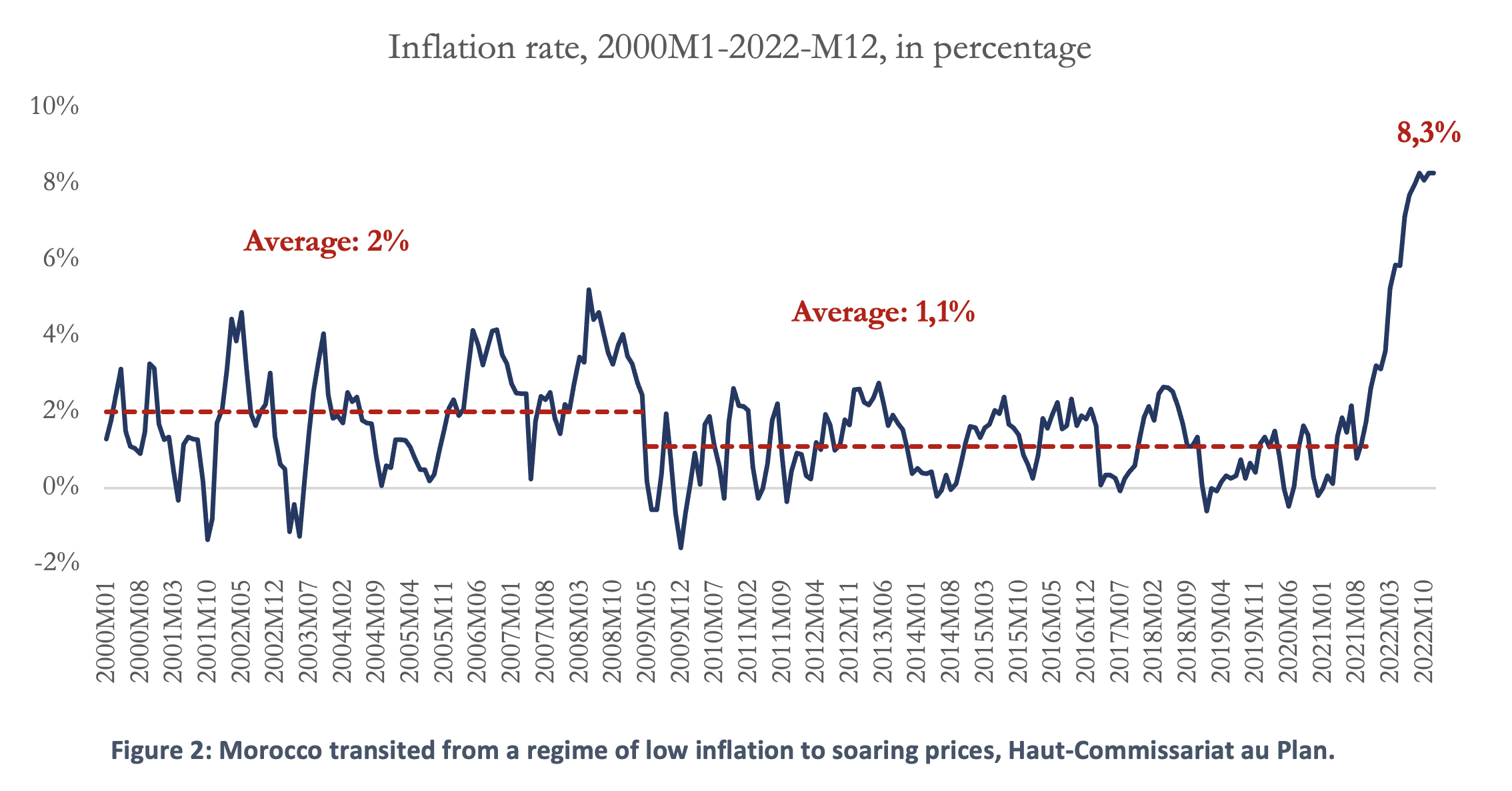
Between 2000 and 2019, Morocco saw two low-inflation regimes, with inflation averaging around 2% and 1.1%, respectively, before and after the Great Recession. During this period, the monetary policy stance was very accommodative, with the Bank Al Maghrib using its main policy rate and reserve requirements to smooth the cycles and achieve its mandate of price stability. The evolution of inflation during this period reflected for the most part the evolution of inflation in partner economies (for the most part in the euro area), which put downward pressure on prices.
Furthermore, fiscal policy has been entrenched in a solid trend of consolidation, since the trough of 2012, leading to a series of reforms, including a partial overhaul of the public subsidy system. Two phases can be observed. The first was of deleveraging, with public debt reaching 55% of GDP on the eve of the 2008 crisis. In the second, in the aftermath, debt steadily increased over 10 years from 2009 to 2018. In 2019, public debt decreased, but the COVID-19 crisis response reversed the course of adjustment.
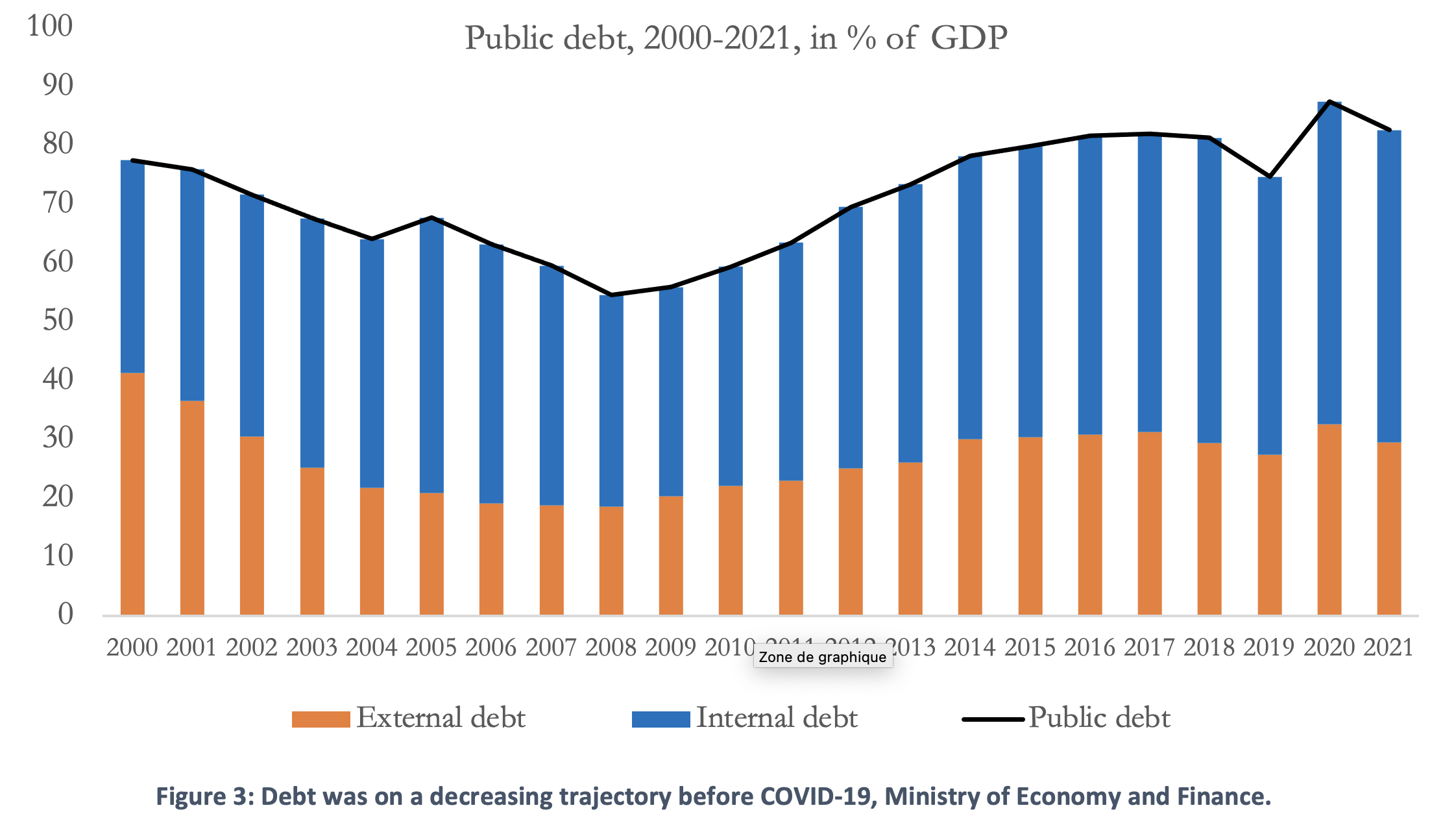
Current economic challenges could impede fiscal consolidation and debt reduction
In 2022, inflation made an astonishing comeback, reaching 6.6% on average. Initially driven by external factors, it started to generalize to all the sectors, and is now solidly entrenched in tradable and non-tradable sectors, with the food segment being impacted severely. Ironically, this inflationary episode has been good news for public finances. Through its magnifying impact on the denominator, it has inflated away the expected increase in the public-debt-to-GDP ratio. It has also driven up tax receipts. As things stand, the public deficit reached 5.1% of GDP in 2022 according early estimates, against an expected figure of 5.9% following the budget act.
However, tightening financing conditions have driven yields upward. The yield curve has significantly shifted upward as the Bank Al Maghrib reacted to increasing prices by pushing up its main rate by 100 basis points in 2022 to anchor expectations, and by another 50 basis points in March 2023. On international markets, the costs of financing have also increased. Based on official projections, fiscal consolidation is expected to happen at a slower pace over the next four years, according to the triennial budgetary programing.
Accelerating reform and mobilizing resources will be key in the near future
The subsequent discussions focused on the next step for the Moroccan economy. Morocco is on the verge of achieving an ambitious social transformation, through the generalization of social protection. This structural reform could have a strong positive impact on growth potential and could set the country on a path towards the establishment of fundamental welfare state principles. However, this will also require significant resource mobilization, given the extent of the expenses that will be incurred. In the short term, reform could have major implications for the future path of the public-debt-to-GDP ratio, while transitioning to a higher growth regime. Multiple scenarios are possible. For instance, based on the World Economic Outlook of October 2022, if inflation returns to normal and the agricultural sector picks up again after two years of drought, then GDP growth should return to its average. Subsequently, some form of fiscal consolidation and debt reduction can be expected. But beyond this central scenario, riskier scenarios are also possible, when taking into account the persistence of inflation in Morocco, and the possible return of severe droughts over the next five to seven years. Such conditions would imply a slow adjustment or even an increase in the public-debt-to-GDP ratio.
Thus, the evolution of public debt will depend on the evolution of the Moroccan economy, which in turns depends on how far the structural reforms will go, and the extent to which public finances will be optimized to mobilize resources.









