Publications /
Opinion
Sub-Saharan Africa’s trade flows increased sharply, multiplying by a factor of five over the past 20 years. Is this boom built on commodities only? My answer is no ! Many countries have increased their integration in global value chains. But, it is also clear that sub-Saharan Africa still has some way to go.
Increased trade boosts for growth
Over the last two decades, the export-to-GDP ratio in sub-Saharan Africa increased from 20½ percent in 1995 to 27½ percent in 2013. This occurred to a great extent thanks to a rising demand for raw materials over that period, but not only, as some non-commodity exporters in the region also recorded impressive progress. In the process, the destination of sub-Saharan African exports changed substantially, with the development of new partnerships with emerging markets such as Brazil, China, and India—China is now the most important single trade partner for sub-Saharan Africa.
Our analysis finds that increased trade integration has had a strong influence on growth in sub-Saharan Africa. Average real GDP per capita growth increased from 2.9 percent in the 1990s, to 4.3 percent in the 2000s. Of that 1.4 percentage point increase, about half was accounted for by higher trade integration.
Still substantial untapped potential
Yet, despite this strong growth, the region’s trade has barely kept up with the expansion of the global trade network over the last 20 years. Of course, this partly reflects lower income levels, generally longer distances, and the specific challenges facing landlocked countries. But even after accounting for those factors, trade flows emanating from sub-Saharan Africa are found to be only half of the magnitude experienced elsewhere, with intra-regional trade only 15–20 percent of what is observed within South and East Asia or Europe.
Global Value Chains: Where are you?
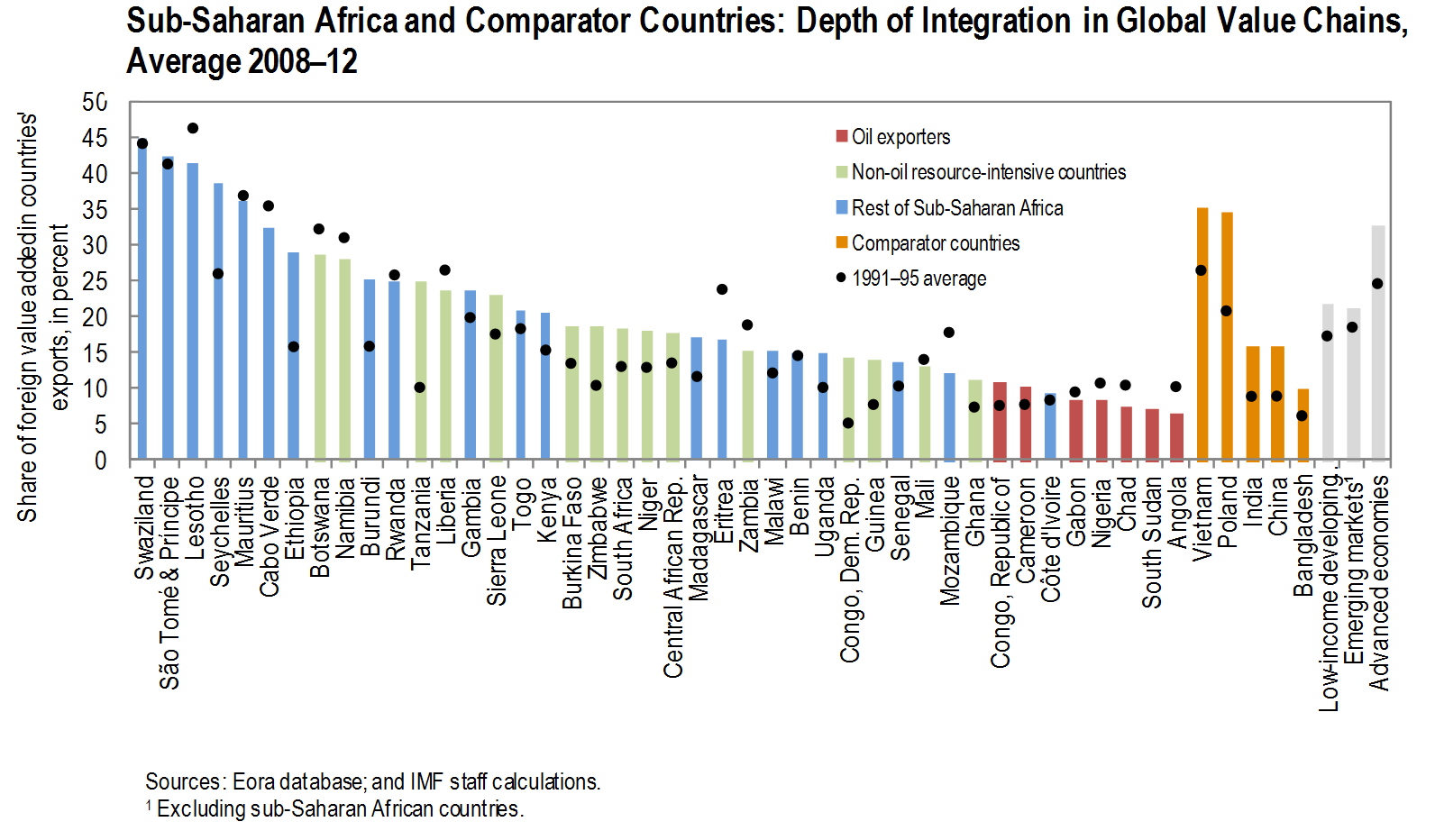
One key dimension of globalization in recent decades has been the development of global value chains—large supply chains in which value is added at each stage of production before crossing borders to be passed on to the next stage. At the global level, deeper integration into global value chains has been accompanied by a rise in income levels over time, most evident in Asia and in Eastern Europe, where countries have successfully plugged themselves into downstream supply chain networks such as processing and assembly trade with imported inputs.
Figure 1 shows that most countries in sub-Saharan Africa have increased their integration in global value chains, as measured by the share of foreign value added in a country’s exports. But while there a substantial degree of heterogeneity across the region, it is also clear that sub-Saharan Africa still has some way to go.
How to seize the opportunity?
How to accelerate the region’s integration into global value chains? The experience of five countries—Tanzania, Ethiopia, Seychelles, South Africa and Kenya—is instructive. These countries stand out, having seen their integration rise over two decades by a magnitude similar to the most successful countries in other regions, such as Poland or Vietnam.
We invite you to read the full OpEd by Roger Nord on Ideas For Development (ID4D) Blog






