Publications /
Opinion
“This time was different” in terms of the monetary policy responses to capital outflow shocks felt by emerging market economies (EMEs), as pointed out by a November 12 Bank for International Settlements bulletin. The pandemic-related global financial shock that hit in March and April led to close to $100 billion leaving EMEs (see my previous article). This was answered by local monetary authorities in ways different from previous episodes.
This time there was even the use of quantitative easing (QE) in some EMEs. That is, the expansion of the central bank balance sheet via acquisition of public or private securities as an additional monetary-financial management tool. Such asset purchase programs may either aim at simply stabilizing asset markets or easing financial conditions (with the term ‘easing’ becoming more applicable in the latter case).
In past financial shocks caused by outbreaks of capital outflows and currency devaluation, emerging central banks were typically forced to tighten their monetary policies to halt the course. This time, in addition to facing strong domestic economic slowdowns, as a result of the health crisis and social distancing associated with COVID-19, aggressive liquidity provision by central banks in advanced economies facilitated a reaction in the opposite direction.
This time, EME central banks cut policy rates. Figure 1 compares interest rate policy reactions to the COVID-19 shock with what happened right after the 2008 global financial crisis and the EME stress period in 2015, when the end of the commodity price boom and a strong appreciation of the dollar sharply tightened financial conditions in EMEs. Having inflation expectations reasonably under control, besides the deflationary nature of the COVID-19 impact, policy rates were lowered as shown.
Figure 1
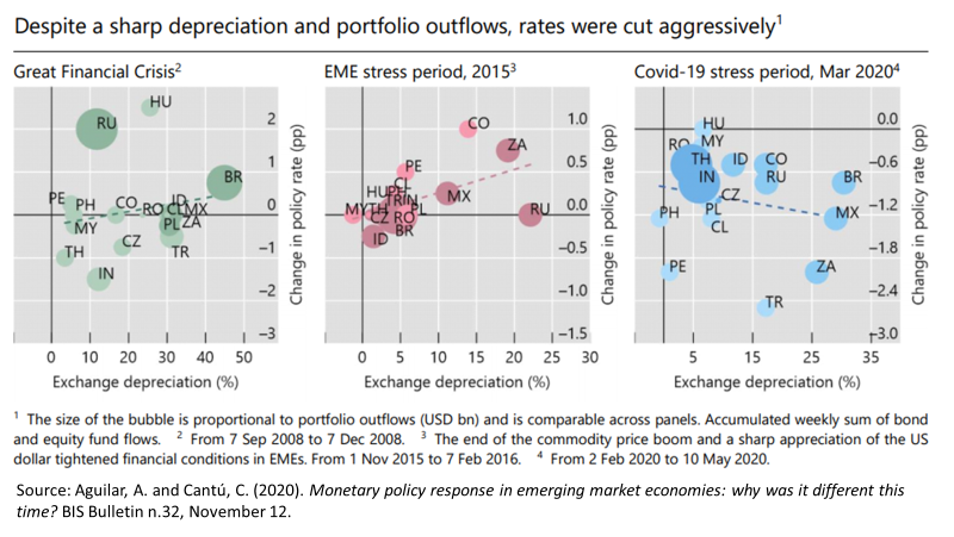
In addition to lowering interest rates, relaxing bank reserve requirements, using foreign reserves to dampen the exchange rate volatility, and term repo actions, the central banks of 18 emerging countries have even launched public bond or private security purchase programs (Figure 2). QE has been for the first time used beyond advanced economies.
Figure 2
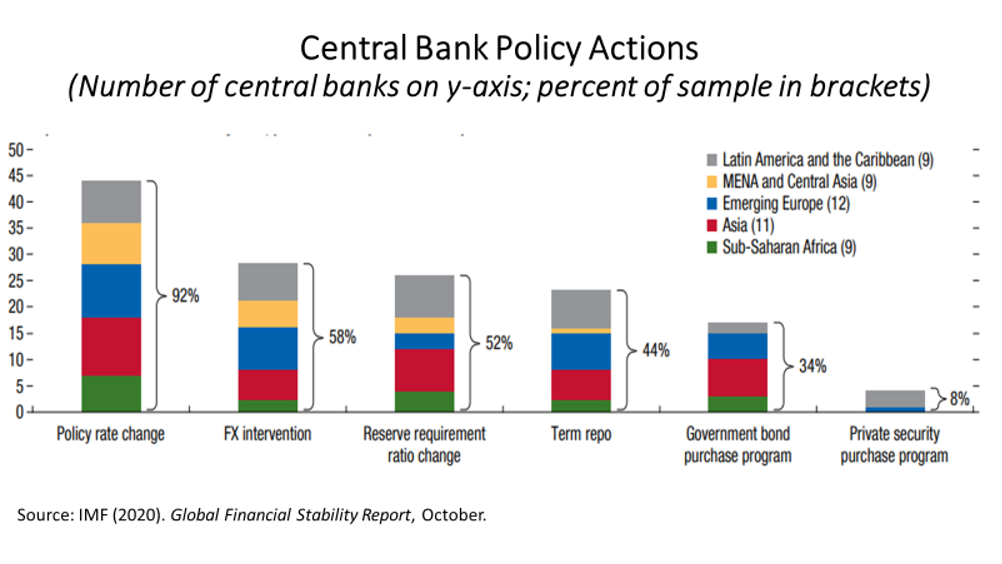
The International Monetary Fund’s latest Global Financial Stability Report assessed the experience with the extended set of EME monetary policy tools. The report distinguishes three groups of EMEs where asset purchase programs were started. In the cases of Chile, Poland, and Hungary, for example, central banks were operating with interest rates already close to their lower bounds and, therefore, it can be said that they were in a similar position to the advanced economies where QE has become “conventional”. India and South Africa, with interest rates well above zero, carried out QE to improve the functioning of secondary bond markets. A third group, on the other hand, aimed to relieve interest pressure on government financing in the circumstances of the epidemic. The central banks of Ghana and Guatemala, for example, bought primary issuance of their countries’ public debt.
Other EMEs resorted to other ways of coping with the sudden liquidity drought and/or financing needs. Brazil used cash buffers the Treasury had within the central bank’s balance sheet, while Mexico increased its external issuance and other Latin American countries engaged pension funds. Issuance was also backloaded to the greatest extent possible.
According to the IMF's assessment, the impact on domestic financial markets was overall positive, helping ease financial conditions. The effects of QE were additional to the direct effects of domestic interest cuts, the indirect effects of the Federal Reserve's asset acquisitions, and an improvement in the global risk appetite from March onward. Arslan et al (2020), in turn, conclude that the actual market impact of asset purchases by EME central banks , pointing to the roles played by initial conditions and how the measures were designed and communicated.
Where used, QE eased stresses in local markets and reduced rates—by somewhere between 0.2 and 0.6 percentage points, according to the IMF report. There were no significant devaluation pressures on exchange rates. This was helped by the fact that in several cases QE corresponded to twist operations, with purchases of long assets being matched with sales of short ones and correspondingly some sterilization of the monetary impact.
The size of asset purchase programs was not large in most cases (Chile, Indonesia, the Philippines, and Poland were exceptions), and the programs were short lived (Figure 3, left panel). They functioned as “circuit breakers”, signaling the central banks as buyers of last resort(Arslan et al, 2020).
QE is more likely to succeed when monetary policy is effectively constrained by its lower bound, inflation expectations are grounded, risks of capital outflows and exchange rate depreciation are deemed low, or the domestic absorption capacity of new bond supply is limited (Figure 3, right panel). Asset purchase programs should be preferentially aimed at restoring confidence in markets, rather than at simply providing monetary stimulus, let alone the monetary financing of fiscal deficits—paradoxically when they are more ‘quantitative stabilizing’ than ‘easing’. Otherwise, programs tend to lead to perceived risks of ‘fiscal dominance’—monetary policy captured by the objective of avoiding fiscal bankruptcy, rather than its own stability targets—or large-scale monetary easing, which would push bond yields up and exchange rates down.
Figure 3

To summarize, the pandemic-related global financial shock has sparked the inclusion of QE as a policy tool also available for EME central banks. Nonetheless, the following caveats should be borne in mind:
- Unless the acquisition of assets by central banks is for monetary financing of primary debt issuance, which is an issue on its own, QE targets the yield structures of interest rates. If there are fragilities leading to high basic, short-term interest rates, QE will not achieve much in terms of results. And the weight of transactions involving longer-term yields in EMEs is lower than in advanced economies
- QE should not raise concerns about ‘fiscal dominance’, because otherwise it will be self-defeating. Capital outflow pressures may exacerbate.
- A prolonged period during which central banks are buyers in local currency bond markets may distort market dynamics. A permanent role of the central bank as a market maker, especially in primary markets, will impair the development of the domestic financial market. Consideration should also be given to the effect of asset purchase programs on possible overvaluation of assets, and on collateral availability in the banking system and its impact on the transmission of the policy rate.
Quantitative easing is now part of the conventional toolbox of EME central banks. But it should not be considered a magic wand.
The opinons expressed in this article belong to the author.










