Publications /
Opinion
The International Monetary Fund’s tenth annual External Sector Report (ESR, August 2021) shows how current account deficits in the global economy widened in 2020 during the pandemic. On the other hand, the ESR also argues that overall, the misalignment between fundamentals and current account balances has not been exacerbated.
The pandemic widened current account imbalances…
The sum of absolute values of current account deficits and surpluses went from 2.8% of global GDP in 2019 to 3.2% last year, reversing a downward trajectory since 2015.
The report points out four major impacts brought about by the pandemic to explain that increase. First, the dramatic drop in travel and tourism has significantly shrunk the balances of countries dependent on tourism receipts, including some Caribbean countries, Thailand, Turkey, Spain, and others.
Additionally, the demand for oil and its price underwent a deep collapse. Although oil prices began a recovery in the second half of the year, oil-exporting countries experienced a sharp drop in current account balances in the year. On the other side, oil-importing countries saw corresponding decreases in their oil trade deficits.
The explosion in the trade of medical products also had effects: a 30% increase in external demand for essential medical supplies needed to fight the pandemic, such as personal protective equipment, and for inputs and raw materials for its production. Importers and exporters of these articles faced corresponding impacts.
Changes in household spending patterns because of the pandemic also had an impact on foreign trade. ‘Staying at home’ meant spending less on contact-intensive services and buying more durable consumer goods, including electronic devices used in teleworking and distance learning. Not by chance, the economic recovery was faster in Asian countries that export such manufactures.
Figure 1 projects where the sum of current account balances in the global economy would have gone were it not for the effects of the pandemic, according to the IMF report:
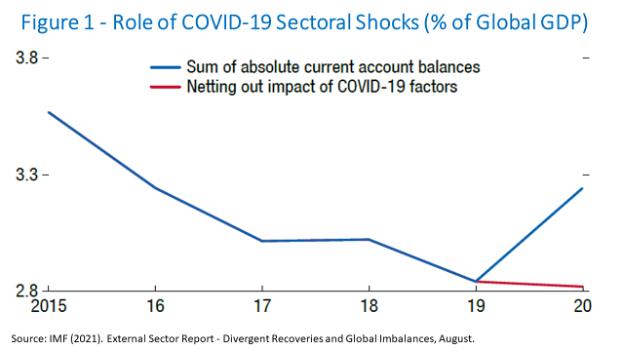
The extraordinarily lax monetary policies adopted by major central banks made the financing of widening current account deficits unproblematic. That was a difference compared to previous crises, when external financing difficulties pushed some countries into recession.
The policies of flattening the pandemic curves led governments to raise large volumes of loans to cover expenses related to health services and economic support for families and companies, which had asymmetric effects on trade balances. Richer economies used their available fiscal space more than poorer economies to implement even more aggressive fiscal policies, borrowing relatively more than poorer economies. The corresponding fall in current account balances, on average, was therefore greater. As a result, the pandemic has slowed the already ‘declining’ flow of funds from the richest countries to the poorest.
… without exacerbating the overall misalignment between fundamentals and current account balances
An important exercise included in every annual IMF External Sector Report goes beyond monitoring of current account balances to examine the extent to which current account imbalances can be considered ‘excessive’ relative to economic fundamentals and appropriate economic policies. The calculation is made for each of the 30 economies considered systemically relevant and covered by the report.
Excessive imbalances are associated with overvaluation of real effective exchange rates, when deficits are larger (or surpluses smaller) than suggested by adequate fundamentals and policies. Symmetrically, there is also an excess when larger surpluses (smaller deficits) than those foreseeable from fundamentals and appropriate policies suggest undervalued real effective exchange rates. Excessive imbalances can generate instability by fueling trade tensions and increasing the likelihood of sharp adjustments in asset prices.
Despite the increase in global current account balances in absolute terms by 0.4 percentage point of global GDP, excessive global imbalances—that is, the sum of the absolute values of the balances considered to diverge from the levels corresponding to fundamentals and adequate policies in the medium term—remained at around 1.2% of world GDP, close to previous levels. Risks and obstacles to recovery in the global economy continue to be strongly associated with the local trajectories of the pandemic, the consequences of which in terms of divergence between countries are still unfolding.
According to the IMF report:
- Twelve of the 30 economies were in 2020 aligned with levels consistent with their medium-term fundamentals and policies considered appropriate: Australia (AUS), Brazil (BRA), China (CHN), Hong Kong (HKG), India (IND), Indonesia (IDN), Italy (ITA), Japan (JPN), South Korea (KOR), the Euro Area (EA), Spain (ESP), and Switzerland (CHE).
- In turn, nine economies exhibited a devalued effective real exchange rate or larger balances—that is, larger surpluses or smaller deficits—than those suggested by fundamentals and adequate policies: Germany (DEU), Malaysia (MYS), Netherlands (NLD), Poland (POL), Sweden (SWE), Thailand (THA), Singapore (SGP), Mexico (MEX), and Russia (RUS).
- The other 9 economies—Argentina (ARG), Belgium (BEL), Canada (CAN), France (FRA), Saudi Arabia (SAU), South Africa (ZAF), United Kingdom (GBR), United States (USA), and Turkey (TUR)—had current account balances that suggested their real effective exchange rates had excessively appreciated, that is, smaller surpluses or deficits larger than those indicated by fundamentals and adequate policies.
Figure 2 gives a snapshot on where the real effective exchange rate (REER) and, accordingly, the positive or negative current account (CA) gaps were last year, relative to what would correspond to fundamentals and appropriate policies in each one of the 30 economies.
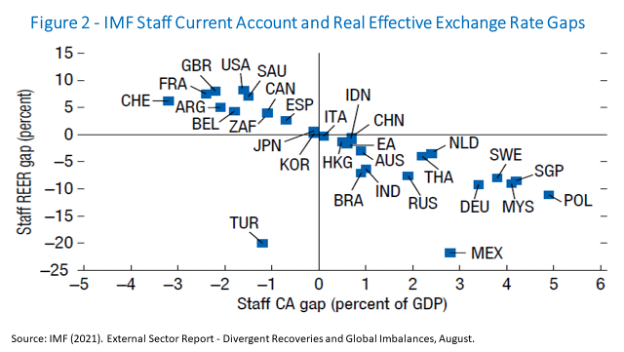
Mexico and Turkey look like outliers for special reasons. Mexico’s external position over-strengthened in 2020 because, while large fiscal expansions took place in other major economies (whose actual fiscal balances went relatively further below their desirable medium-term levels), Mexico had a non-significant fiscal response to the pandemic and an additional weakening of the domestic investment climate.
Turkey’s external position in 2020 was moderately weaker than the level implied by medium-term fundamentals and desirable policies. In Turkey’s case, according to the ESR:
“Expansionary monetary policy and rapid provision of credit by state-owned banks put pressure on the lira last year through dollarization, import, and financial account channels, which led in turn to sales of foreign exchange reserves to support the lira. Despite the marked real exchange rate depreciation, the CA deficit resurfaced because of lower exports (including tourism) and robust imports (including gold). The monetary tightening beginning in late 2020 saw a return of capital inflows and modest reserves buildup, but outflows and reserves losses resumed in March 2021, amid rising policy uncertainty and lira depreciation. Policy uncertainty, large gross external financing needs, and relatively low reserves increase Turkey’s vulnerability to shocks. Only over time will the REER undervaluation, with its usual lags, help move the current account back toward its norm, aided by less expansionary policies.”
Whither current account imbalances?
The evolution of current account balances will depend on the fiscal trajectories ahead. The United States—the biggest economy among the cases of appreciated REER—is expected to delay adjustments, judging by the fiscal packages sought by the Biden administration. In turn, Germany—and its devalued REER—would have an even more imbalanced position if it resorted to quick fiscal adjustments. A tightening of global financial conditions with an impact on capital flows to emerging and developing economies could also affect their balances (although factors mitigating those risks can be pointed out).
Going forward, countries with excessive current account balances should seek to shrink their budget deficits over the medium term, and to implement reforms that increase their competitiveness. Meanwhile, economies with excessive current account surpluses and some fiscal space should adopt policies to strengthen recovery and growth over the medium term, including through greater public investment.
Meanwhile, as highlighted by Martin Kaufman and Daniel Leigh:
"A synchronized push in global investment or health spending to end the pandemic and support recovery could have considerable effects on global growth without raising global balances."
The opinions expressed in this article belong to the author.











