Publications /
Policy Brief
- The earthquake’s overall impact on growth is estimated to be around -0.24% of GDP in 2023.
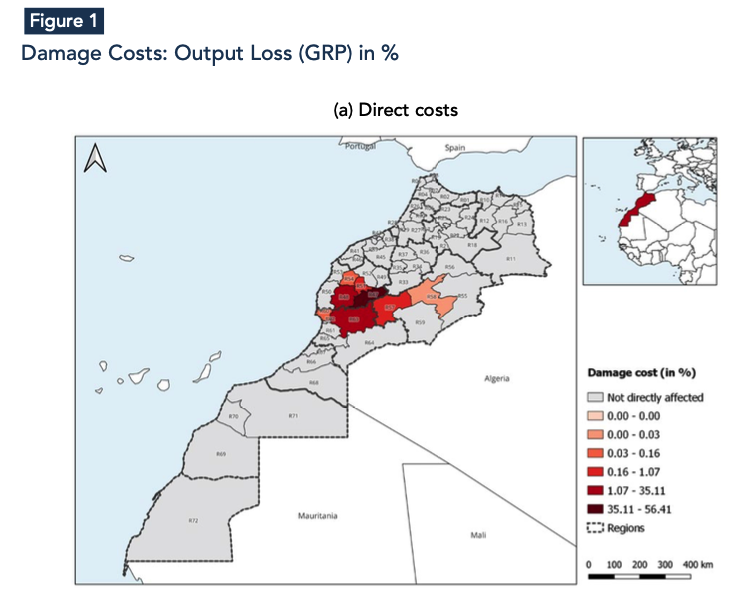
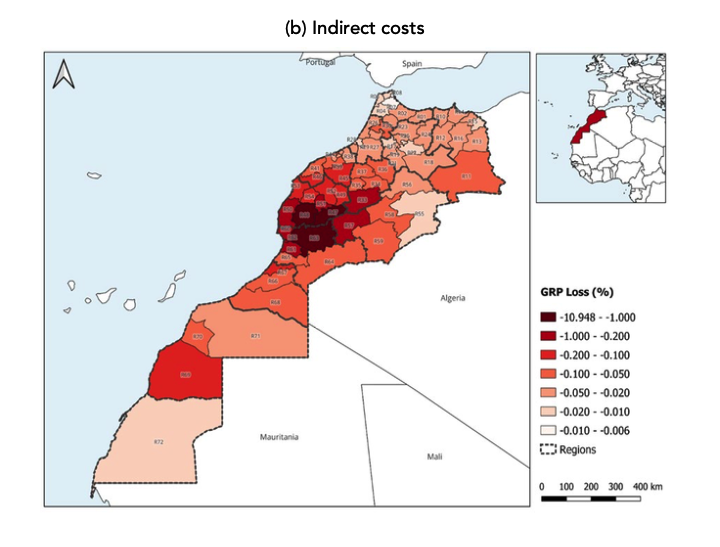
- Due to the spatial concentration of the earthquake, Al-Haouz province and the Marrakesh region experienced Gross Regional Product (GRP) losses of -10.2% and -1.3%, respectively.
- The 120 billion Moroccan dirhams (MAD) recovery program will have only mild positive impacts on overall macroeconomic growth from 2023 to 2028 but will significantly benefit the High Atlas region due to the reallocation of resources from non-affected to affected areas.
- The overall macroeconomic impact is significantly influenced by the decision regarding the financing package, whether through new funds (debt) or investment reallocation.
- However, this decision results in minor differences in the substantial positive impacts on the High Atlas region.
Main takeaways
- The scale of the disaster and the availability of resources will influence the duration of the recovery.
- A small region may bounce back more quickly, especially if there is effective local support and swift response measures in place.
- Additional resources needed beyond those required for basic rebuilding are needed to upgrade infrastructure as part of a regional development plan for the High Atlas region.
1. Introduction
The impact of the 2023 Al-Haouz earthquake extended beyond human casualties to include substantial material damage. In response, Moroccan authorities have launched an ambitious 5-year reconstruction plan, the “Program for Reconstruction and Rehabilitation of Affected Areas,” with a projected budget of 120 billion MAD, equivalent to 11.7 billion USD. The resources will target emergency aid to families and financial assistance for housing, as well as infrastructure rebuilding and upgrading, with the aim of uplifting affected areas and restoring them to their initial state. Additional resources will be dedicated to regional development and the promotion of economic activities in the High Atlas provinces. The program seeks to enhance infrastructure, promote agricultural and tourist activities, rehabilitate urban areas and ancient cities, and improve the quality of public services.
At PCNS, we developed a comprehensive report providing an economic assessment of the earthquake’s impacts, as well as the potential effects of the reconstruction plan. This policy brief summarizes our main findings.
2. Direct Damages: 2023
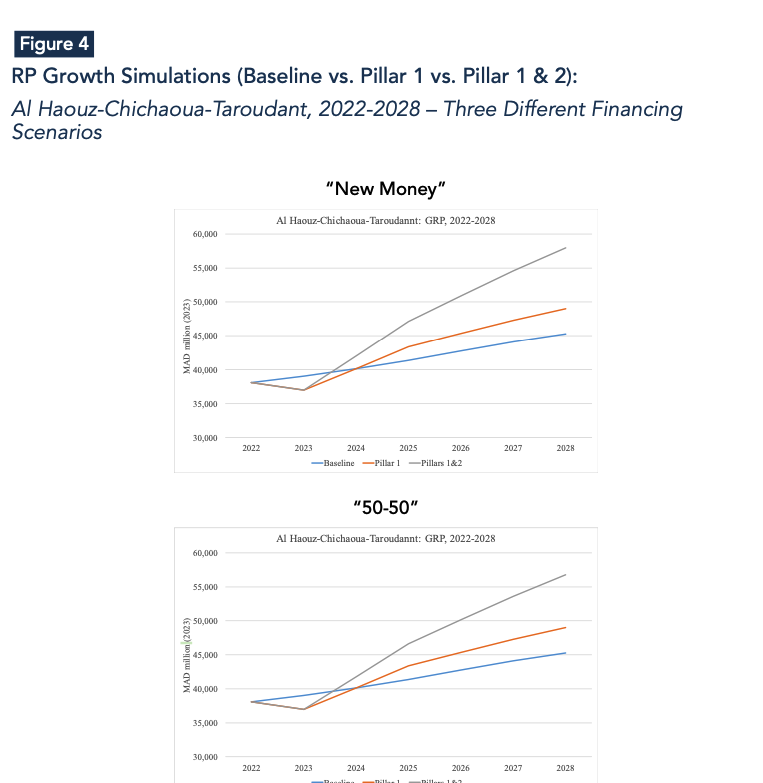
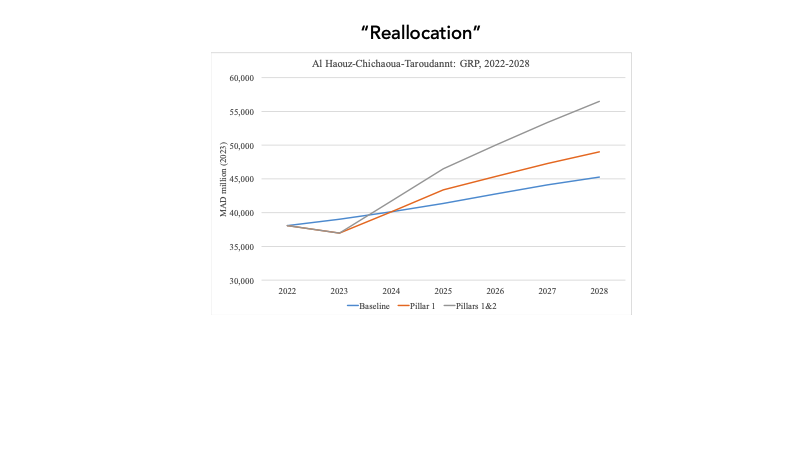
Quantifying economic losses is essential to gauge individual and community vulnerability, evaluate the worthiness of mitigation, determine the appropriate level of disaster assistance, improve recovery decisions, and inform insurers of their potential liability (Rose, 2004). The direct cost of the earthquake for the affected provinces represents the estimated expenses on infrastructure required to restore the infrastructure to its pre-earthquake level. In this regard, the economic infrastructure loss was concentrated around the earthquake’s epicenter in Al-Haouz, followed by neighboring provinces, mainly Taroudant and Chichaoua (Figure 1a).
Regarding the indirect cost of the earthquake, when comparing the baseline scenario (an artificial counterfactual assuming the earthquake not happened) with the factual occurrence (the earthquake actually happening), simulation results indicate a GDP loss of approximately 0.24%, equivalent to around 3 billion MAD in 2023. Consequently, economic activity in the Marrakesh region dropped by 1.3%, while Al-Haouz province lost roughly 10.2% of its GRP. The remaining provinces of Morocco recorded lower magnitude losses, proportional to their respective linkages with the affected provinces (Figure 1b). Al-Haouz province registered 53% of the total GRP loss among the six most affected regions, totaling roughly 1.2 billion MAD. Following closely is the Taroudant province with a GRP loss of 739 million MAD. The remaining affected provinces—Chichaoua, Marrakech, Ouarzazate and Azilal— collectively faced a GRP loss of around 305 million MAD.
3. Impact of the “Program for Reconstruction and Rehabilitation of Affected Areas”
Moroccan authorities have launched a 5-year reconstruction plan, allocating 120 billion MAD. The budget will be divided into two main pillars: 22 billion MAD for emergency assistance to households and infrastructure rebuilding, and 98 billion MAD earmarked for the upgrading of the High Atlas region.
3.1. First Pillar: 22 Billion MAD
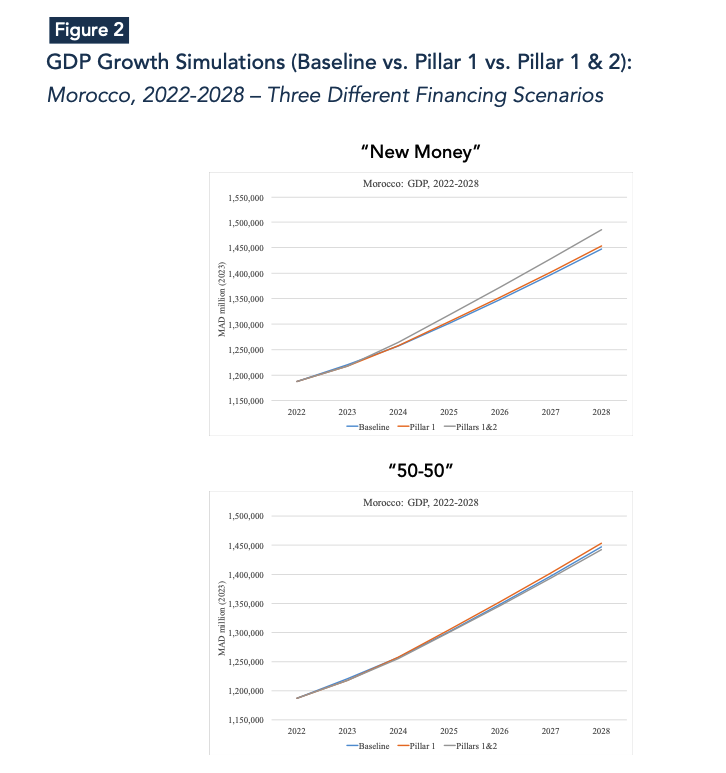
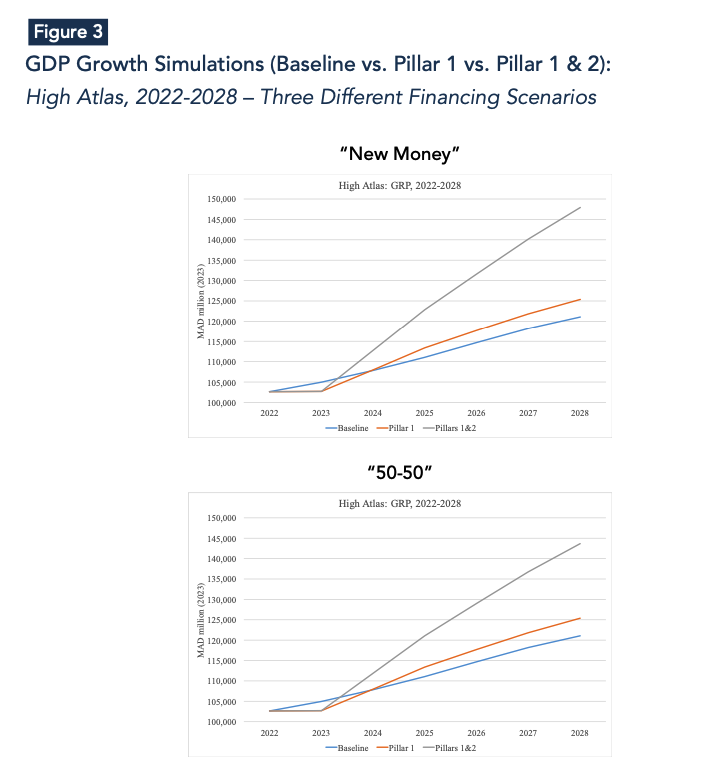
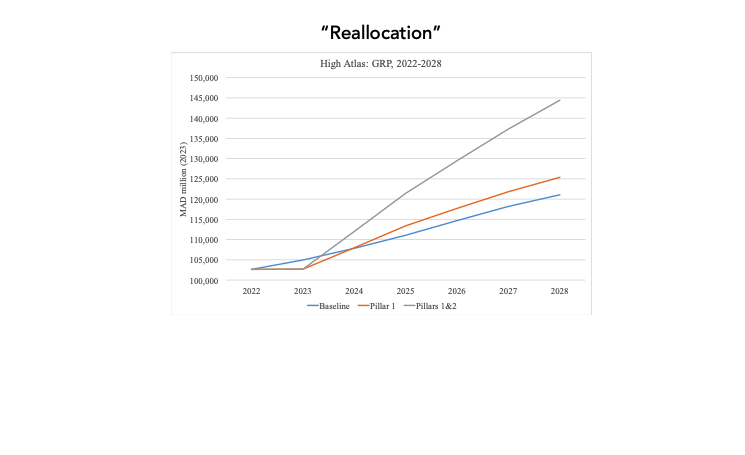
The first pillar of the reconstruction plan includes emergency aid to households and financial assistance for housing totaling 8 billion MAD over the period 2023-2024, and 14 billion MAD for infrastructure rebuilding and upgrading from 2023 to 2028. Simulation results for the first pillar indicate that injecting 22 billion MAD into the Moroccan economy will lead to a 0.1 percentage point increase in overall growth at the country level and a 1.2 percentage point increase in growth for the High Atlas provinces on average between 2024 and 2028. Transitioning from the national to the provincial level, the difference between the new growth trajectory (pillar 1) and the baseline scenario (IMF pre-disaster growth projections) increases significantly in relative magnitude (Figures 2-4). This is primarily because the most affected provinces—Al Haouz, Chichaoua, and Taroudant—will receive the majority of the 22 billion MAD recovery plan.
3.2. Second Pillar: 98 Billion MAD
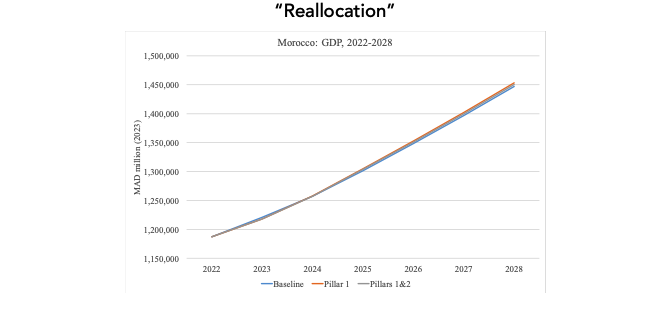
The second pillar encompasses 98 billion MAD aimed at stimulating and fostering economic activity across the entire High Atlas region. Given the absence of precise information on the allocation of these funds, we will consider three hypothetical scenarios. The first scenario assumes the entire 98 billion MAD will be financed through new resources, such as debt. The second scenario involves splitting the 98 billion MAD evenly between new funding (50%) and reallocation of existing investments (50%). The third scenario envisions the funding entirely through reallocation of existing investments.
National Impact
Growth simulations at the national level, incorporating the effects of both pillars (1 & 2), suggest that the overall impact varies significantly based on the financing scenario. This ranges from an average 0.4 percentage points for the “New Money” scenario to a 0.03 percentage points for the “Reallocation” scenario over the period 2024-2028.
The stark contrast in magnitude between the two extreme scenarios—New Money and complete investment reallocation—arises because the former represents a hypothetical scenario where the government injects approximately 10% of GDP into the economy as new funds. In contrast, the latter involves a straightforward reallocation of investment funds from unaffected to affected areas, which is expected to generate only modest positive impacts on national growth.
Regional Impact
For the High Atlas provinces, growth simulations incorporating the impacts of both pillars (1 & 2) consistently show positive effects on growth across all financing scenarios. This is because these provinces are receivers of funding, irrespective of its source, leading to minimal variations among the different financing scenarios.
4. Discussion
We assessed the economic impacts of the Al-Haouz earthquake in terms of direct and indirect production losses at the national, regional, and provincial levels using a multisectoral and multiregional model for Morocco. Our results indicate that this natural disaster will cost 0.24% of Morocco’s GDP in 2023, resulting in a 1.3% drop in Marrakesh-Safi’s GRP and a 10.2% decline in economic activity in the Al-Haouz province. Considering these estimations, we can infer that the earthquake of September 8 was more of a human tragedy with moderate economic losses, especially at the macroeconomic level. This conclusion is further supported by the analysis of high-frequency financial indicators, which demonstrate the resilient nature of the Moroccan economy following the disaster.
Secondly, we examined the “Program for Reconstruction and Rehabilitation of Affected Areas”, which allocates 120 billion MAD for short-term emergency aid to households, financial assistance for housing reconstruction, and medium to long-term infrastructure rebuilding and upgrading of the affected areas, as well as the promotion of economic activity in the remaining High Atlas provinces. We assessed the economic impact of the recovery program through its two main pillars while considering different hypotheses for the financing scheme of the second pillar, ranging from a new injection of money into the economy (i.e. debt) to a complete reallocation of investments from non-affected to affected areas. Given Morocco’s focus on maintaining macroeconomic stability and debt sustainability, it is reasonable to assume that the financing of the second pillar (98 billion MAD) will come primarily from investment reallocation rather than increased indebtedness.
Focusing on this scenario, our results indicate that the 120 billion MAD recovery plan will have only a mildly positive impact on growth at the national level, with an average increase of 0.03 percentage points over the period 2024-2028. For the High Atlas provinces, significant growth increases are expected due to the recovery plan, regardless of the financing scenario.
Finally, policymakers will need to confront a trade-off between efficiency and equity when reallocating resources from non-affected (and highly productive) areas to affected (and less productive) areas. Considering the policy intentions to reduce regional disparities and the necessity to assist underdeveloped regions in catching up with the rest of the country’s development stage, it may be prudent to prioritize equity over efficiency in these circumstances.










